Chapter 20: Prioritization
Chapter 20: Prioritization | 第二十章:优先级排序
In complex, dynamic environments, Agents frequently encounter numerous potential actions, conflicting goals, and limited resources. Without a defined process for determining the subsequent action, the agents may experience reduced efficiency, operational delays, or failures to achieve key objectives. The prioritization pattern addresses this issue by enabling agents to assess and rank tasks, objectives, or actions based on their significance, urgency, dependencies, and established criteria. This ensures the agents concentrate efforts on the most critical tasks, resulting in enhanced effectiveness and goal alignment.
在复杂多变的环境中,智能体常常面临大量潜在行动、相互冲突的目标以及有限的资源。如果缺乏明确的流程来决定下一步行动,智能体可能会出现效率降低、运行延迟,甚至无法实现关键目标等问题。优先级排序模式通过让智能体根据重要性、紧迫性、依赖关系和既定标准来评估和排序任务、目标或行动,解决了这一问题。这确保智能体能够将精力集中在最关键的任务上,从而提升效能并实现与目标的对齐。
Prioritization Pattern Overview | 优先级排序模式概述
Agents employ prioritization to effectively manage tasks, goals, and sub-goals, guiding subsequent actions. This process facilitates informed decision-making when addressing multiple demands, prioritizing vital or urgent activities over less critical ones. It is particularly relevant in real-world scenarios where resources are constrained, time is limited, and objectives may conflict.
智能体使用优先级排序来有效管理任务、目标和子目标,从而指导后续行动。这一过程有助于在面对多种需求时做出明智决策,优先处理重要或紧急的活动,而非不太关键的事项。这在资源受限、时间紧迫且目标可能相互冲突的现实场景中尤为重要。
The fundamental aspects of agent prioritization typically involve several elements. First, criteria definition establishes the rules or metrics for task evaluation. These may include urgency (time sensitivity of the task), importance (impact on the primary objective), dependencies (whether the task is a prerequisite for others), resource availability (readiness of necessary tools or information), cost/benefit analysis (effort versus expected outcome), and user preferences for personalized agents. Second, task evaluation involves assessing each potential task against these defined criteria, utilizing methods ranging from simple rules to complex scoring or reasoning by LLMs. Third, scheduling or selection logic refers to the algorithm that, based on the evaluations, selects the optimal next action or task sequence, potentially utilizing a queue or an advanced planning component. Finally, dynamic re-prioritization allows the agent to modify priorities as circumstances change, such as the emergence of a new critical event or an approaching deadline, ensuring agent adaptability and responsiveness.
智能体优先级排序的基本要素通常包括以下几个方面。首先,标准定义为任务评估建立规则或指标,可能包括紧迫性(任务的时间敏感度)、重要性(对主要目标的影响)、依赖关系(该任务是否是其他任务的前提)、资源可用性(所需工具或信息的就绪状态)、成本收益分析(投入与预期产出的对比)以及个性化智能体的用户偏好。其次,任务评估是根据这些定义的标准对每个潜在任务进行评估,使用的方法从简单规则到大语言模型(LLM)的复杂评分或推理不等。第三,调度或选择逻辑是指基于评估结果选择最优下一步行动或任务序列的算法,可能使用队列或高级规划组件。最后,动态重新排序允许智能体在情况发生变化时(如出现新的关键事件或截止日期临近)调整优先级,确保智能体的适应性和响应能力。
Prioritization can occur at various levels: selecting an overarching objective (high-level goal prioritization), ordering steps within a plan (sub-task prioritization), or choosing the next immediate action from available options (action selection). Effective prioritization enables agents to exhibit more intelligent, efficient, and robust behavior, especially in complex, multi-objective environments. This mirrors human team organization, where managers prioritize tasks by considering input from all members.
优先级排序可以发生在多个层次:选择总体目标(高层目标优先级排序)、安排计划中的步骤顺序(子任务优先级排序),或从可用选项中选择下一个立即行动(行动选择)。有效的优先级排序使智能体能够展现更智能、高效和稳健的行为,特别是在复杂的多目标环境中。这与人类团队组织方式类似,管理者会综合考虑所有成员的意见来确定任务优先级。
Practical Applications & Use Cases | 实际应用场景
In various real-world applications, AI agents demonstrate a sophisticated use of prioritization to make timely and effective decisions.
在各种实际应用中,AI 智能体展现出了对优先级排序的精妙运用,以做出及时有效的决策。
-
Automated Customer Support: Agents prioritize urgent requests, like system outage reports, over routine matters, such as password resets. They may also give preferential treatment to high-value customers.
-
自动化客户支持:智能体优先处理紧急请求(如系统故障报告),而非常规事务(如密码重置)。它们还可能优先服务高价值客户。
-
Cloud Computing: AI manages and schedules resources by prioritizing allocation to critical applications during peak demand, while relegating less urgent batch jobs to off-peak hours to optimize costs.
-
云计算:AI 通过在高峰需求期间优先为关键应用分配资源,同时将不太紧急的批处理任务安排在非高峰时段来管理和调度资源,从而优化成本。
-
Autonomous Driving Systems: Continuously prioritize actions to ensure safety and efficiency. For example, braking to avoid a collision takes precedence over maintaining lane discipline or optimizing fuel efficiency.
-
自动驾驶系统:持续对行动进行优先级排序以确保安全和效率。例如,制动避免碰撞的优先级高于保持车道纪律或优化燃油效率。
-
Financial Trading: Bots prioritize trades by analyzing factors like market conditions, risk tolerance, profit margins, and real-time news, enabling prompt execution of high-priority transactions.
-
金融交易:交易机器人通过分析市场状况、风险承受能力、利润率和实时新闻等因素来确定交易优先级,从而快速执行高优先级交易。
-
Project Management: AI agents prioritize tasks on a project board based on deadlines, dependencies, team availability, and strategic importance.
-
项目管理:AI 智能体根据截止日期、依赖关系、团队可用性和战略重要性,对项目看板上的任务进行优先级排序。
-
Cybersecurity: Agents monitoring network traffic prioritize alerts by assessing threat severity, potential impact, and asset criticality, ensuring immediate responses to the most dangerous threats.
-
网络安全:监控网络流量的智能体通过评估威胁严重程度、潜在影响和资产关键性来确定警报优先级,确保立即应对最危险的威胁。
-
Personal Assistant AIs: Utilize prioritization to manage daily lives, organizing calendar events, reminders, and notifications according to user-defined importance, upcoming deadlines, and current context.
-
个人助理 AI:利用优先级排序来管理日常生活,根据用户定义的重要性、即将到来的截止日期和当前情境组织日历事件、提醒和通知。
These examples collectively illustrate how the ability to prioritize is fundamental to the enhanced performance and decision-making capabilities of AI agents across a wide spectrum of situations.
这些示例共同说明了优先级排序能力对于 AI 智能体在各种情境中提升性能和决策能力的重要性。
Hands-On Code Example | 使用 LangChain 的实战代码
The following demonstrates the development of a Project Manager AI agent using LangChain. This agent facilitates the creation, prioritization, and assignment of tasks to team members, illustrating the application of large language models with bespoke tools for automated project management.
以下演示了如何使用 LangChain 开发项目经理 AI 智能体。该智能体能够创建、排序任务优先级并将任务分配给团队成员,展示了大语言模型与定制工具在自动化项目管理中的应用。
import os
import asyncio
from typing import List, Optional, Dict, Type
from dotenv import load_dotenv
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_core.tools import Tool
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.agents import AgentExecutor, create_react_agent
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemory
# --- 0. Configuration and Setup ---
# Loads the OPENAI_API_KEY from the .env file.
load_dotenv()
# The ChatOpenAI client automatically picks up the API key from the environment.
llm = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0.5, model="gpt-4o-mini")
# --- 1. Task Management System ---
class Task(BaseModel):
"""Represents a single task in the system."""
id: str
description: str
priority: Optional[str] = None # P0, P1, P2
assigned_to: Optional[str] = None # Name of the worker
class SuperSimpleTaskManager:
"""An efficient and robust in-memory task manager."""
def __init__(self):
# Use a dictionary for O(1) lookups, updates, and deletions.
self.tasks: Dict[str, Task] = {}
self.next_task_id = 1
def create_task(self, description: str) -> Task:
"""Creates and stores a new task."""
task_id = f"TASK-{self.next_task_id:03d}"
new_task = Task(id=task_id, description=description)
self.tasks[task_id] = new_task
self.next_task_id += 1
print(f"DEBUG: Task created - {task_id}: {description}")
return new_task
def update_task(self, task_id: str, **kwargs) -> Optional[Task]:
"""Safely updates a task using Pydantic's model_copy."""
task = self.tasks.get(task_id)
if task:
# Use model_copy for type-safe updates.
update_data = {k: v for k, v in kwargs.items() if v is not None}
updated_task = task.model_copy(update=update_data)
self.tasks[task_id] = updated_task
print(f"DEBUG: Task {task_id} updated with {update_data}")
return updated_task
print(f"DEBUG: Task {task_id} not found for update.")
return None
def list_all_tasks(self) -> str:
"""Lists all tasks currently in the system."""
if not self.tasks:
return "No tasks in the system."
task_strings = []
for task in self.tasks.values():
task_strings.append(
f"ID: {task.id}, Desc: '{task.description}', "
f"Priority: {task.priority or 'N/A'}, "
f"Assigned To: {task.assigned_to or 'N/A'}"
)
return "Current Tasks:\n" + "\n".join(task_strings)
task_manager = SuperSimpleTaskManager()
# --- 2. Tools for the Project Manager Agent ---
# Use Pydantic models for tool arguments for better validation and clarity.
class CreateTaskArgs(BaseModel):
description: str = Field(description="A detailed description of the task.")
class PriorityArgs(BaseModel):
task_id: str = Field(description="The ID of the task to update, e.g., 'TASK-001'.")
priority: str = Field(description="The priority to set. Must be one of: 'P0', 'P1', 'P2'.")
class AssignWorkerArgs(BaseModel):
task_id: str = Field(description="The ID of the task to update, e.g., 'TASK-001'.")
worker_name: str = Field(description="The name of the worker to assign the task to.")
def create_new_task_tool(description: str) -> str:
"""Creates a new project task with the given description."""
task = task_manager.create_task(description)
return f"Created task {task.id}: '{task.description}'."
def assign_priority_to_task_tool(task_id: str, priority: str) -> str:
"""Assigns a priority (P0, P1, P2) to a given task ID."""
if priority not in ["P0", "P1", "P2"]:
return "Invalid priority. Must be P0, P1, or P2."
task = task_manager.update_task(task_id, priority=priority)
return f"Assigned priority {priority} to task {task.id}." if task else f"Task {task_id} not found."
def assign_task_to_worker_tool(task_id: str, worker_name: str) -> str:
"""Assigns a task to a specific worker."""
task = task_manager.update_task(task_id, assigned_to=worker_name)
return f"Assigned task {task.id} to {worker_name}." if task else f"Task {task_id} not found."
# All tools the PM agent can use
pm_tools = [
Tool(
name="create_new_task",
func=create_new_task_tool,
description="Use this first to create a new task and get its ID.",
args_schema=CreateTaskArgs
),
Tool(
name="assign_priority_to_task",
func=assign_priority_to_task_tool,
description="Use this to assign a priority to a task after it has been created.",
args_schema=PriorityArgs
),
Tool(
name="assign_task_to_worker",
func=assign_task_to_worker_tool,
description="Use this to assign a task to a specific worker after it has been created.",
args_schema=AssignWorkerArgs
),
Tool(
name="list_all_tasks",
func=task_manager.list_all_tasks,
description="Use this to list all current tasks and their status."
),
]
# --- 3. Project Manager Agent Definition ---
pm_prompt_template = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", """You are a focused Project Manager LLM agent. Your goal is to manage project tasks efficiently.
When you receive a new task request, follow these steps:
1. First, create the task with the given description using the `create_new_task` tool. You must do this first to get a `task_id`.
2. Next, analyze the user's request to see if a priority or an assignee is mentioned.
- If a priority is mentioned (e.g., "urgent", "ASAP", "critical"), map it to P0. Use `assign_priority_to_task`.
- If a worker is mentioned, use `assign_task_to_worker`.
3. If any information (priority, assignee) is missing, you must make a reasonable default assignment (e.g., assign P1 priority and assign to 'Worker A').
4. Once the task is fully processed, use `list_all_tasks` to show the final state.
Available workers: 'Worker A', 'Worker B', 'Review Team'
Priority levels: P0 (highest), P1 (medium), P2 (lowest)
"""),
("placeholder", "{chat_history}"),
("human", "{input}"),
("placeholder", "{agent_scratchpad}")
])
# Create the agent executor
pm_agent = create_react_agent(llm, pm_tools, pm_prompt_template)
pm_agent_executor = AgentExecutor(
agent=pm_agent,
tools=pm_tools,
verbose=True,
handle_parsing_errors=True,
memory=ConversationBufferMemory(memory_key="chat_history", return_messages=True)
)
# --- 4. Simple Interaction Flow ---
async def run_simulation():
print("--- Project Manager Simulation ---")
# Scenario 1: Handle a new, urgent feature request
print("\n[User Request] I need a new login system implemented ASAP. It should be assigned to Worker B.")
await pm_agent_executor.ainvoke({"input": "Create a task to implement a new login system. It's urgent and should be assigned to Worker B."})
print("\n" + "-"*60 + "\n")
# Scenario 2: Handle a less urgent content update with fewer details
print("[User Request] We need to review the marketing website content.")
await pm_agent_executor.ainvoke({"input": "Manage a new task: Review marketing website content."})
print("\n--- Simulation Complete ---")
# Run the simulation
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(run_simulation())
This code implements a simple task management system using Python and LangChain, designed to simulate a project manager agent powered by a large language model.
该代码使用 Python 和 LangChain 实现了一个简单的任务管理系统,旨在模拟由大语言模型驱动的项目经理智能体。
The system employs a SuperSimpleTaskManager class to efficiently manage tasks within memory, utilizing a dictionary structure for rapid data retrieval. Each task is represented by a Task Pydantic model, which encompasses attributes such as a unique identifier, a descriptive text, an optional priority level (P0, P1, P2), and an optional assignee designation.Memory usage varies based on task type, the number of workers, and other contributing factors. The task manager provides methods for task creation, task modification, and retrieval of all tasks.
系统采用 SuperSimpleTaskManager 类在内存中高效管理任务,利用字典结构实现快速数据检索。每个任务由 Task Pydantic 模型表示,包含唯一标识符、描述文本、可选优先级(P0、P1、P2)和可选分配对象等属性。内存使用量因任务类型、工作人员数量和其他因素而异。任务管理器提供任务创建、修改和检索所有任务的方法。
The agent interacts with the task manager via a defined set of Tools. These tools facilitate the creation of new tasks, the assignment of priorities to tasks, the allocation of tasks to personnel, and the listing of all tasks. Each tool is encapsulated to enable interaction with an instance of the SuperSimpleTaskManager. Pydantic models are utilized to delineate the requisite arguments for the tools, thereby ensuring data validation.
智能体通过一组定义好的工具与任务管理器交互。这些工具用于创建新任务、分配任务优先级、将任务分配给人员以及列出所有任务。每个工具都被封装以便与 SuperSimpleTaskManager 实例交互。使用 Pydantic 模型来定义工具所需的参数,从而确保数据验证。
An AgentExecutor is configured with the language model, the toolset, and a conversation memory component to maintain contextual continuity. A specific ChatPromptTemplate is defined to direct the agent's behavior in its project management role. The prompt instructs the agent to initiate by creating a task, subsequently assigning priority and personnel as specified, and concluding with a comprehensive task list. Default assignments, such as P1 priority and 'Worker A', are stipulated within the prompt for instances where information is absent.
通过配置语言模型、工具集和对话记忆组件来构建 AgentExecutor,以保持上下文连续性。定义了特定的 ChatPromptTemplate 来指导智能体在项目管理角色中的行为。提示指示智能体首先创建任务,然后根据指定分配优先级和人员,最后提供完整的任务列表。在缺少信息的情况下,提示中规定了默认分配(如 P1 优先级和「Worker A」)。
The code incorporates a simulation function (run_simulation) of asynchronous nature to demonstrate the agent's operational capacity. The simulation executes two distinct scenarios: the management of an urgent task with designated personnel, and the management of a less urgent task with minimal input. The agent's actions and logical processes are outputted to the console due to the activation of verbose=True within the AgentExecutor.
代码包含一个异步模拟函数(run_simulation)来演示智能体的运行能力。该模拟执行两个不同的场景:管理指定人员的紧急任务,以及管理输入最少的非紧急任务。由于在 AgentExecutor 中激活了 verbose=True,智能体的动作和逻辑过程会输出到控制台。
At a Glance | 要点速览
What: AI agents operating in complex environments face a multitude of potential actions, conflicting goals, and finite resources. Without a clear method to determine their next move, these agents risk becoming inefficient and ineffective. This can lead to significant operational delays or a complete failure to accomplish primary objectives. The core challenge is to manage this overwhelming number of choices to ensure the agent acts purposefully and logically.
问题所在:在复杂环境中运行的 AI 智能体面临大量潜在行动、相互冲突的目标和有限的资源。如果没有明确的方法来确定下一步行动,这些智能体可能会变得低效和无效。这可能导致严重的运行延迟,甚至完全无法实现主要目标。核心挑战是管理这些压倒性的选择,以确保智能体有目的性和逻辑性地行动。
Why: The Prioritization pattern provides a standardized solution for this problem by enabling agents to rank tasks and goals. This is achieved by establishing clear criteria such as urgency, importance, dependencies, and resource cost. The agent then evaluates each potential action against these criteria to determine the most critical and timely course of action. This Agentic capability allows the system to dynamically adapt to changing circumstances and manage constrained resources effectively. By focusing on the highest-priority items, the agent's behavior becomes more intelligent, robust, and aligned with its strategic goals.
解决之道:优先级排序模式通过让智能体对任务和目标进行排序,为这一问题提供了标准化解决方案。这是通过建立明确标准(如紧迫性、重要性、依赖关系和资源成本)来实现的。然后,智能体根据这些标准评估每个潜在行动,以确定最关键和最及时的行动方案。这种具智能体特性的能力使系统能够动态适应变化的情况,并有效管理受限资源。通过专注于最高优先级项目,智能体的行为变得更加智能、稳健,并与其战略目标保持一致。
Rule of thumb: Use the Prioritization pattern when an Agentic system must autonomously manage multiple, often conflicting, tasks or goals under resource constraints to operate effectively in a dynamic environment.
经验法则:当具智能体特性的系统需要在资源受限的情况下自主管理多个(通常相互冲突的)任务或目标,以便在动态环境中有效运行时,应使用优先级排序模式。
Visual summary:
可视化总结:
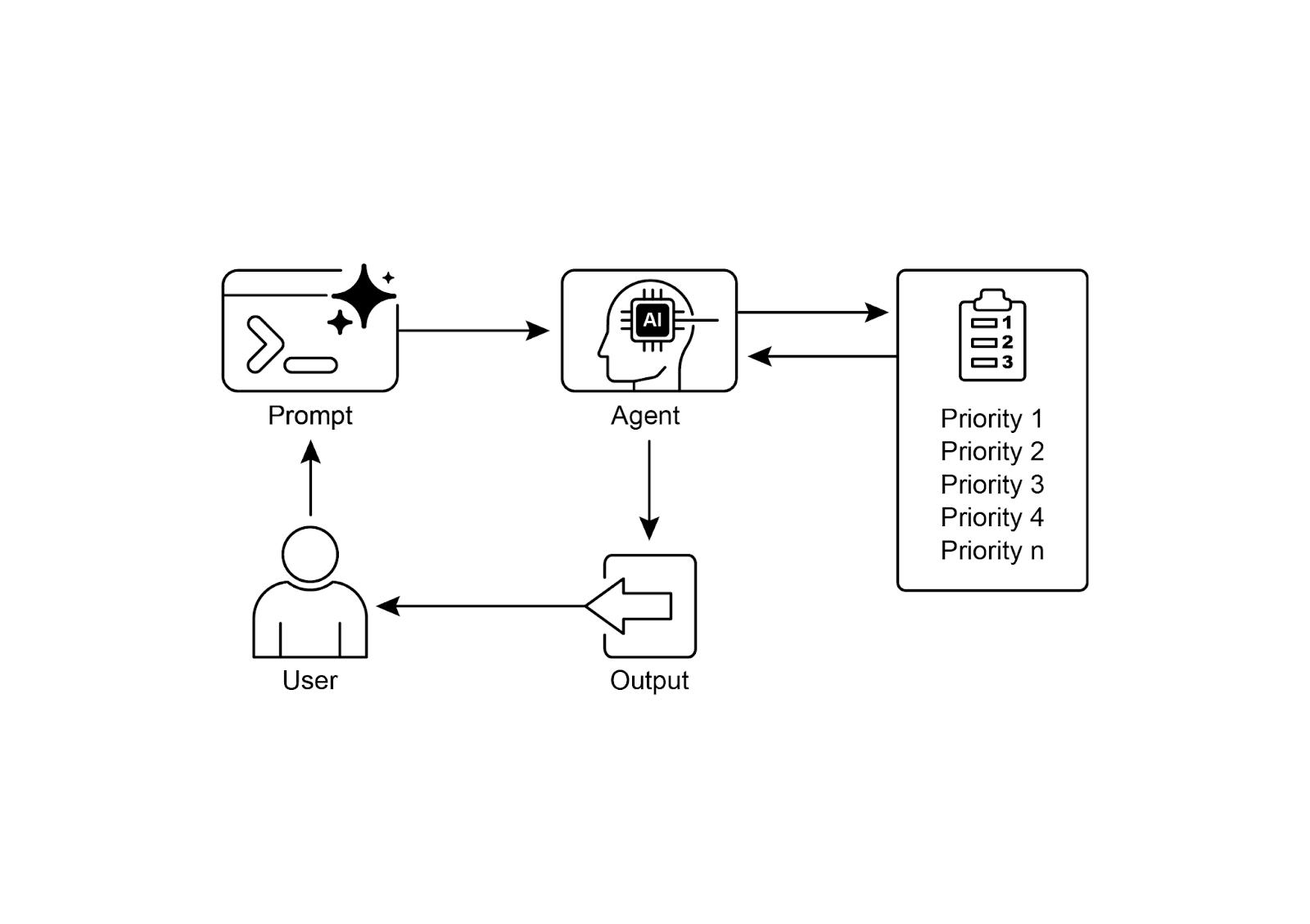
图 1:优先级排序设计模式
Key Takeaways | 核心要点
-
Prioritization enables AI agents to function effectively in complex, multi-faceted environments.
-
优先级排序使 AI 智能体能够在复杂多变的环境中有效运作。
-
Agents utilize established criteria such as urgency, importance, and dependencies to evaluate and rank tasks.
-
智能体利用既定标准(如紧迫性、重要性和依赖关系)来评估和排序任务。
-
Dynamic re-prioritization allows agents to adjust their operational focus in response to real-time changes.
-
动态重新排序使智能体能够根据实时变化调整其运行重点。
-
Prioritization occurs at various levels, encompassing overarching strategic objectives and immediate tactical decisions.
-
优先级排序发生在多个层次,涵盖总体战略目标和即时战术决策。
-
Effective prioritization results in increased efficiency and improved operational robustness of AI agents.
-
有效的优先级排序能够提升 AI 智能体的效率和运行稳健性。
Conclusions | 结语
In conclusion, the prioritization pattern is a cornerstone of effective agentic AI, equipping systems to navigate the complexities of dynamic environments with purpose and intelligence. It allows an agent to autonomously evaluate a multitude of conflicting tasks and goals, making reasoned decisions about where to focus its limited resources. This agentic capability moves beyond simple task execution, enabling the system to act as a proactive, strategic decision-maker. By weighing criteria such as urgency, importance, and dependencies, the agent demonstrates a sophisticated, human-like reasoning process.
总之,优先级排序模式是高效的具智能体特性的 AI 的基石,使系统能够有目的性和智能性地应对动态环境的复杂性。它使智能体能够自主评估大量相互冲突的任务和目标,就如何集中有限资源做出理性决策。这种具智能体特性的能力超越了简单的任务执行,使系统能够成为主动的战略决策者。通过权衡紧迫性、重要性和依赖关系等标准,智能体展现出复杂的、类人的推理过程。
A key feature of this agentic behavior is dynamic re-prioritization, which grants the agent the autonomy to adapt its focus in real-time as conditions change. As demonstrated in the code example, the agent interprets ambiguous requests, autonomously selects and uses the appropriate tools, and logically sequences its actions to fulfill its objectives. This ability to self-manage its workflow is what separates a true agentic system from a simple automated script. Ultimately, mastering prioritization is fundamental for creating robust and intelligent agents that can operate effectively and reliably in any complex, real-world scenario.
这种具智能体特性的行为的一个关键特征是动态重新排序,它赋予智能体在条件变化时实时调整其关注点的自主性。正如代码示例所展示的,智能体能够解读模糊的请求,自主选择并使用适当的工具,并合理安排其行动顺序以实现目标。这种自我管理工作流程的能力是真正具智能体特性的系统与简单自动化脚本的区别所在。归根结底,掌握优先级排序是创建能够在任何复杂现实场景中有效且可靠运行的稳健智能体的基础。
References | 参考文献
-
Examining the Security of Artificial Intelligence in Project Management: A Case Study of AI-driven Project Scheduling and Resource Allocation in Information Systems Projects ; https://www.irejournals.com/paper-details/1706160
人工智能在项目管理中的安全性研究:信息系统项目中 AI 驱动的项目调度与资源分配案例研究
-
AI-Driven Decision Support Systems in Agile Software Project Management: Enhancing Risk Mitigation and Resource Allocation; https://www.mdpi.com/2079-8954/13/3/208
敏捷软件项目管理中的 AI 驱动决策支持系统:增强风险缓解与资源分配