Chapter 15: Inter Agent Communication
Chapter 15: Inter-Agent Communication (A2A) | 第 15 章: 智能体间通信 (A2A)
Individual AI agents often face limitations when tackling complex, multifaceted problems, even with advanced capabilities. To overcome this, Inter-Agent Communication (A2A) enables diverse AI agents, potentially built with different frameworks, to collaborate effectively. This collaboration involves seamless coordination, task delegation, and information exchange. Google's A2A protocol is an open standard designed to facilitate this universal communication. This chapter will explore A2A, its practical applications, and its implementation within the Google ADK.
单个 AI 智能体在处理复杂、多方面的问题时, 即使能力很强, 也常常面临局限性。为了克服这一挑战, 智能体间通信 (Inter-Agent Communication, A2A) 使基于不同框架构建的 AI 智能体能够有效协作。这种协作涉及无缝的协调、任务委派和信息交换。Google 的 A2A 协议是旨在促进这种通用通信的开放标准。本章将探讨 A2A、其实际应用及其在 Google ADK 中的实现。
Inter-Agent Communication Pattern Overview | 智能体间通信模式概述
The Agent2Agent (A2A) protocol is an open standard designed to enable communication and collaboration between different AI agent frameworks. It ensures interoperability, allowing AI agents developed with technologies like LangGraph, CrewAI, or Google ADK to work together regardless of their origin or framework differences. A2A is supported by a range of technology companies and service providers, including Atlassian, Box, LangChain, MongoDB, Salesforce, SAP, and ServiceNow. Microsoft plans to integrate A2A into Azure AI Foundry and Copilot Studio, demonstrating its commitment to open protocols. Additionally, Auth0 and SAP are integrating A2A support into their platforms and agents. As an open-source protocol, A2A welcomes community contributions to facilitate its evolution and widespread adoption.
Agent2Agent (A2A) 协议是旨在实现不同 AI 智能体框架之间通信与协作的开放标准。它确保了互操作性, 允许使用 LangGraph、CrewAI 或 Google ADK 等技术开发的 AI 智能体协同工作, 而不受其来源或框架差异的影响。A2A 得到了众多技术公司和服务提供商的支持, 包括 Atlassian、Box、LangChain、MongoDB、Salesforce、SAP 和 ServiceNow。Microsoft 计划将 A2A 集成到 Azure AI Foundry 和 Copilot Studio 中, 表明了其对开放协议的承诺。此外, Auth0 和 SAP 正在将 A2A 支持集成到其平台和智能体中。作为开源协议, A2A 欢迎社区贡献, 以促进其发展和广泛采用。
Core Concepts of A2A | A2A 的核心概念
The A2A protocol provides a structured approach for agent interactions, built upon several core concepts. A thorough grasp of these concepts is crucial for anyone developing or integrating with A2A-compliant systems. The foundational pillars of A2A include Core Actors, Agent Card, Agent Discovery, Communication and Tasks, Interaction mechanisms, and Security, all of which will be reviewed in detail.
A2A 协议为智能体交互提供了结构化方法, 建立在几个核心概念之上。深入理解这些概念对于开发或集成 A2A 兼容系统至关重要。A2A 的基础组成部分包括核心参与者、智能体卡片、智能体发现、通信与任务、交互机制以及安全性, 接下来将对这些核心组成部分进行详细介绍。
Core Actors | 核心参与者
Core Actors: A2A involves three main entities:
核心参与者: A2A 涉及三个主要实体:
-
User: Initiates requests for agent assistance.
-
用户 (User): 发起智能体协助请求。
-
A2A Client (Client Agent): An application or AI agent that acts on the user's behalf to request actions or information.
-
A2A 客户端 (客户端智能体): 代表用户请求操作或信息的应用程序或 AI 智能体。
-
A2A Server (Remote Agent): An AI agent or system that provides an HTTP endpoint to process client requests and return results. The remote agent operates as an "opaque" system, meaning the client does not need to understand its internal operational details.
-
A2A 服务器 (远程智能体): 提供 HTTP 端点以处理客户端请求并返回结果的 AI 智能体或系统。远程智能体作为「不透明」系统运行, 这意味着客户端无需了解其内部操作细节。
Agent Card
智能体卡片
Agent Card: An agent's digital identity is defined by its Agent Card, usually a JSON file. This file contains key information for client interaction and automatic discovery, including the agent's identity, endpoint URL, and version. It also details supported capabilities like streaming or push notifications, specific skills, default input/output modes, and authentication requirements. Below is an example of an Agent Card for a WeatherBot.
智能体卡片: 智能体的数字身份由其智能体卡片 (Agent Card) 定义, 通常是 JSON 文件。该文件包含用于客户端交互和自动发现的关键信息, 包括智能体的身份、端点 URL 和版本。它还详细说明了支持的功能 (如流式传输或推送通知)、特定技能、默认输入/输出模式以及身份验证要求。以下是 WeatherBot 的智能体卡片示例。
{
"name": "WeatherBot",
"description": "Provides accurate weather forecasts and historical data.",
"url": "http://weather-service.example.com/a2a",
"version": "1.0.0",
"capabilities": {
"streaming": true,
"pushNotifications": false,
"stateTransitionHistory": true
},
"authentication": {
"schemes": [
"apiKey"
]
},
"defaultInputModes": [
"text"
],
"defaultOutputModes": [
"text"
],
"skills": [
{
"id": "get_current_weather",
"name": "Get Current Weather",
"description": "Retrieve real-time weather for any location.",
"inputModes": [
"text"
],
"outputModes": [
"text"
],
"examples": [
"What's the weather in Paris?",
"Current conditions in Tokyo"
],
"tags": [
"weather",
"current",
"real-time"
]
},
{
"id": "get_forecast",
"name": "Get Forecast",
"description": "Get 5-day weather predictions.",
"inputModes": [
"text"
],
"outputModes": [
"text"
],
"examples": [
"5-day forecast for New York",
"Will it rain in London this weekend?"
],
"tags": [
"weather",
"forecast",
"prediction"
]
}
]
}
Agent discovery | 智能体发现
Agent discovery: it allows clients to find Agent Cards, which describe the capabilities of available A2A Servers. Several strategies exist for this process:
智能体发现 (Agent discovery): 它允许客户端找到描述可用 A2A 服务器能力的智能体卡片。此过程存在多种策略:
Well-Known URI: Agents host their Agent Card at a standardized path (e.g., /.well-known/agent.json). This approach offers broad, often automated, accessibility for public or domain-specific use.
Well-Known URI: 智能体在标准化路径 (例如/.well-known/agent.json) 上托管其智能体卡片。这种方法为公共或特定领域的使用提供了广泛且通常是自动化的可访问性。
Curated Registries: These provide a centralized catalog where Agent Cards are published and can be queried based on specific criteria. This is well-suited for enterprise environments needing centralized management and access control.
托管注册中心 (Curated Registries): 这些注册中心提供了一个集中的目录, 智能体卡片在此发布, 并可根据特定标准进行查询。这非常适合需要集中管理和访问控制的企业环境。
Direct Configuration: Agent Card information is embedded or privately shared. This method is appropriate for closely coupled or private systems where dynamic discovery isn't crucial.
直接配置 (Direct Configuration): 智能体卡片信息被嵌入或私下共享。此方法适用于动态发现不那么重要的紧密耦合或私有系统。
Regardless of the chosen method, it is important to secure Agent Card endpoints. This can be achieved through access control, mutual TLS (mTLS), or network restrictions, especially if the card contains sensitive (though non-secret) information.
无论选择哪种方法, 保护智能体卡片端点都很重要。这可以通过访问控制、双向 TLS (mutual TLS, mTLS) 或网络限制来实现, 特别是当卡片包含敏感 (尽管非机密) 信息时。
Communications and Tasks | 通信与任务
In the A2A framework, communication is structured around asynchronous tasks, which represent the fundamental units of work for long-running processes. Each task is assigned a unique identifier and moves through a series of states-such as submitted, working, or completed-a design that supports parallel processing in complex operations. Communication between agents occurs through a Message.
在 A2A 框架中, 通信围绕异步任务构建, 异步任务是长时间运行流程的基本工作单元。每个任务都被分配唯一标识符, 并经历一系列状态——例如已提交、处理中或已完成——这种设计支持复杂操作中的并行处理。智能体之间的通信通过消息 (Message) 进行。
This communication contains attributes, which are key-value metadata describing the message (like its priority or creation time), and one or more parts, which carry the actual content being delivered, such as plain text, files, or structured JSON data. The tangible outputs generated by an agent during a task are called artifacts. Like messages, artifacts are also composed of one or more parts and can be streamed incrementally as results become available. All communication within the A2A framework is conducted over HTTP(S) using the JSON-RPC 2.0 protocol for payloads. To maintain continuity across multiple interactions, a server-generated contextId is used to group related tasks and preserve context.
消息包含 attributes 和一个或多个 part。attributes 是描述消息的键值元数据, 如其优先级或创建时间。part 承载实际交付的内容, 如纯文本、文件或结构化 JSON 数据。智能体在任务期间生成的具体输出被称为 artifacts。与消息类似, artifacts 也由一个或多个部分组成, 并且可以在结果可用时以增量方式流式传输。A2A 框架内的所有通信都通过 HTTP(S) 进行, 并使用 JSON-RPC 2.0 协议作为负载。为了在多次交互中保持连续性, 使用服务器生成的 contextId 来对相关任务进行分组并保留上下文。
Interaction Mechanisms | 交互机制
Request/Response (Polling) Server-Sent Events (SSE). A2A provides multiple interaction methods to suit a variety of AI application needs, each with a distinct mechanism:
A2A 提供了多种交互方法以适应各种 AI 应用需求, 每种方法都有其独特的机制:
- Synchronous Request/Response: For quick, immediate operations. In this model, the client sends a request and actively waits for the server to process it and return a complete response in a single, synchronous exchange.
- 同步请求/响应: 用于快速、即时的操作。在这种模型中, 客户端发送请求并主动等待服务器处理, 服务器在单个同步交换中返回完整响应。
- Asynchronous Polling: Suited for tasks that take longer to process. The client sends a request, and the server immediately acknowledges it with a "working" status and a task ID. The client is then free to perform other actions and can periodically poll the server by sending new requests to check the status of the task until it is marked as "completed" or "failed."
- 异步轮询: 适用于需要较长时间处理的任务。客户端发送一个请求, 服务器立即以 “处理中” 状态和任务 ID 进行确认。然后客户端可以自由执行其他操作, 并可以通过发送新请求定期轮询服务器以检查任务状态, 直到任务被标记为 “已完成” 或 “失败”。
- Streaming Updates (Server-Sent Events - SSE): Ideal for receiving real-time, incremental results. This method establishes a persistent, one-way connection from the server to the client. It allows the remote agent to continuously push updates, such as status changes or partial results, without the client needing to make multiple requests.
- 流式更新 (服务器发送事件-SSE): 非常适合接收实时、增量的结果。此方法建立了一个从服务器到客户端的持久性单向连接。它允许远程智能体持续推送更新, 例如状态变更或部分结果, 而无需客户端发出多个请求。
- Push Notifications (Webhooks): Designed for very long-running or resource-intensive tasks where maintaining a constant connection or frequent polling is inefficient. The client can register a webhook URL, and the server will send an asynchronous notification (a "push") to that URL when the task's status changes significantly (e.g., upon completion).
- 推送通知 (Webhooks): 专为运行时间很长或资源密集型的任务设计, 在这些任务中维持长连接或频繁轮询效率低。客户端可以注册 webhook URL, 当任务状态发生重大变化 (例如完成时), 服务器将向该 URL 发送异步通知 (「推送」)。
The Agent Card specifies whether an agent supports streaming or push notification capabilities. Furthermore, A2A is modality-agnostic, meaning it can facilitate these interaction patterns not just for text, but also for other data types like audio and video, enabling rich, multimodal AI applications. Both streaming and push notification capabilities are specified within the Agent Card.
智能体卡片指定了智能体是否支持流式传输或推送通知功能。此外, A2A 是模态无关 (modality-agnostic) 的, 这意味着它不仅可以提供文本的交互模式, 还可以支持音频和视频等其他数据类型, 从而实现丰富的多模态 AI 应用。流式传输和推送通知功能都在智能体卡片中指定。
# 同步请求示例
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": "1",
"method": "sendTask",
"params": {
"id": "task-001",
"sessionId": "session-001",
"message": {
"role": "user",
"parts": [
{
"type": "text",
"text": "What is the exchange rate from USD to EUR?"
}
]
},
"acceptedOutputModes": [
"text/plain"
],
"historyLength": 5
}
}
The synchronous request uses the sendTask method, where the client asks for and expects a single, complete answer to its query. In contrast, the streaming request uses the sendTaskSubscribe method to establish a persistent connection, allowing the agent to send back multiple, incremental updates or partial results over time.
同步请求示例使用 sendTask 方法, 客户端发起请求并期望得到单一、完整的响应。相比之下, 流式请求使用 sendTaskSubscribe 方法建立持久连接, 允许智能体随时间推移发回多个增量更新或部分结果。
# 流式请求示例
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": "2",
"method": "sendTaskSubscribe",
"params": {
"id": "task-002",
"sessionId": "session-001",
"message": {
"role": "user",
"parts": [
{
"type": "text",
"text": "What's the exchange rate for JPY to GBP today?"
}
]
},
"acceptedOutputModes": [
"text/plain"
],
"historyLength": 5
}
}
Security | 安全性
Inter-Agent Communication (A2A): Inter-Agent Communication (A2A) is a vital component of system architecture, enabling secure and seamless data exchange among agents. It ensures robustness and integrity through several built-in mechanisms.
智能体间通信 (A2A): 智能体间通信 (A2A) 是系统架构的重要组成部分, 它实现了智能体之间安全、无缝的数据交换。通过多种内置机制, 它确保了系统的稳健性和完整性。
Mutual Transport Layer Security (TLS): Encrypted and authenticated connections are established to prevent unauthorized access and data interception, ensuring secure communication.
双向传输层安全 (TLS): 建立加密和认证的连接, 以防止未经授权的访问和数据拦截, 确保通信安全。
Comprehensive Audit Logs: All inter-agent communications are meticulously recorded, detailing information flow, involved agents, and actions. This audit trail is crucial for accountability, troubleshooting, and security analysis.
全面的审计日志: 所有智能体间的通信都被详细记录, 包括信息流、涉及的智能体和执行的操作。这个审计跟踪对于问责、故障排查和安全分析至关重要。
Agent Card Declaration: Authentication requirements are explicitly declared in the Agent Card, a configuration artifact outlining the agent's identity, capabilities, and security policies. This centralizes and simplifies authentication management.
智能体卡片声明: 身份验证要求在智能体卡片中明确声明, 这是概述智能体身份、能力和安全策略的配置工件。这使得身份验证管理得以集中和简化。
Credential Handling: Agents typically authenticate using secure credentials like OAuth 2.0 tokens or API keys, passed via HTTP headers. This method prevents credential exposure in URLs or message bodies, enhancing overall security.
凭证处理: 智能体通常使用安全的凭证 (如 OAuth 2.0 令牌或 API 密钥) 进行身份验证, 这些凭证通过 HTTP 标头传递。这种方法可以防止凭证在 URL 或消息体中暴露, 从而增强整体安全性。
A2A vs. MCP
A2A 与 MCP 的对比
A2A is a protocol that complements Anthropic's Model Context Protocol (MCP) (see Fig. 1). While MCP focuses on structuring context for agents and their interaction with external data and tools, A2A facilitates coordination and communication among agents, enabling task delegation and collaboration.
A2A 是与 Anthropic 模型上下文协议 (Model Context Protocol, MCP) 互补的协议 (见图 1)。MCP 侧重于为智能体及其与外部数据和工具的交互构建上下文, 而 A2A 则促进智能体之间的协调与通信, 从而实现任务委派和协作。
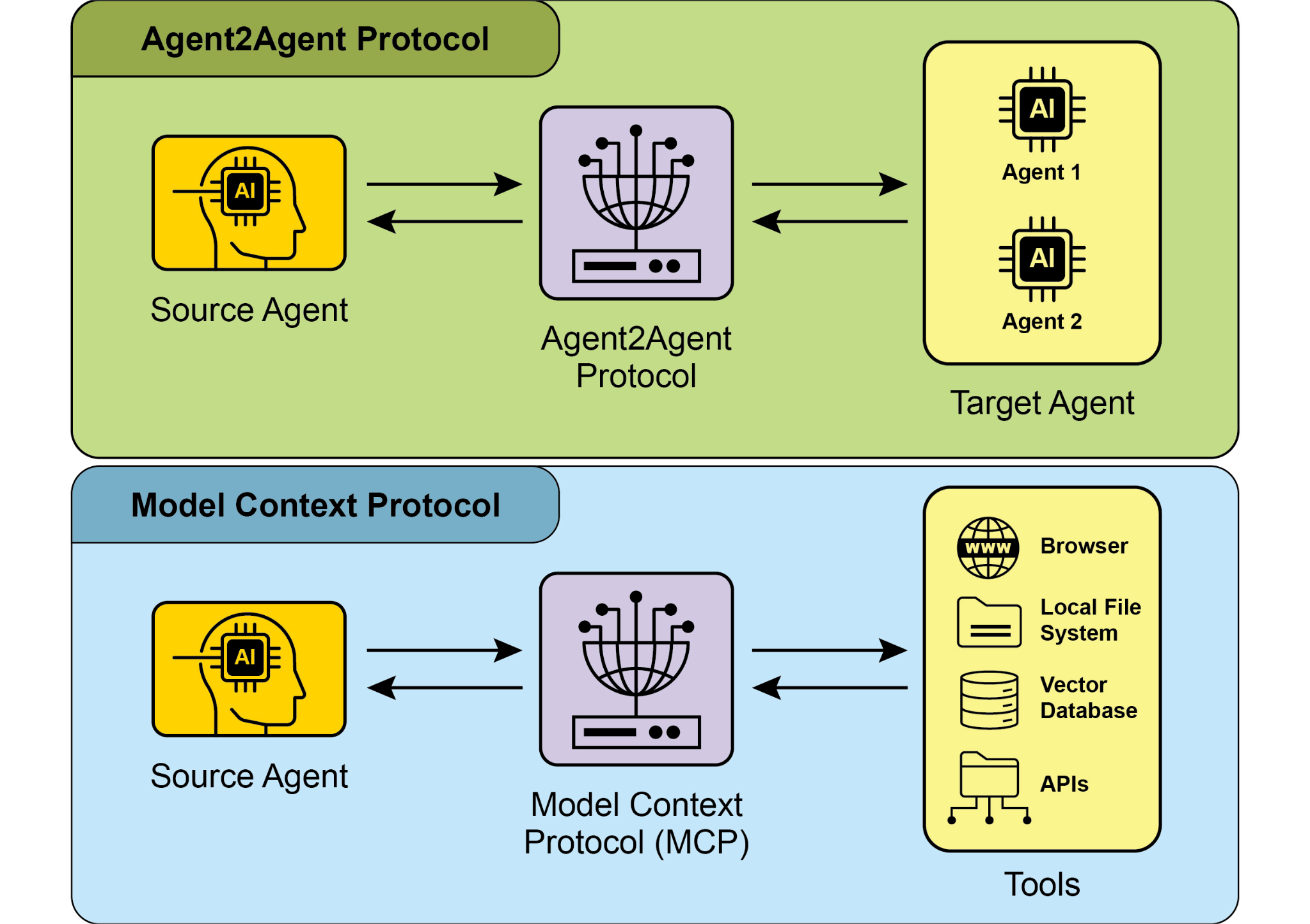 Fig.1: Comparison A2A and MCP Protocols
Fig.1: Comparison A2A and MCP Protocols
图 1: A2A 和 MCP 协议的比较
The goal of A2A is to enhance efficiency, reduce integration costs, and foster innovation and interoperability in the development of complex, multi-agent AI systems. Therefore, a thorough understanding of A2A's core components and operational methods is essential for its effective design, implementation, and application in building collaborative and interoperable AI agent systems.
A2A 的目标是在开发复杂的多智能体 AI 系统时提高效率、降低集成成本, 并促进创新和互操作性。因此, 深入理解 A2A 的核心组件和操作方法对于在构建协作和互操作的 AI 智能体系统中有效设计、实施和应用至关重要。
Practical Applications & Use Cases | 实际应用与使用场景
Inter-Agent Communication is indispensable for building sophisticated AI solutions across diverse domains, enabling modularity, scalability, and enhanced intelligence.
智能体间通信对于在不同领域构建复杂的 AI 解决方案是不可或缺的, 它能实现模块化、可扩展性并增强智能。
Multi-Framework Collaboration: A2A's primary use case is enabling independent AI agents, regardless of their underlying frameworks (e.g., ADK, LangChain, CrewAI), to communicate and collaborate. This is fundamental for building complex multi-agent systems where different agents specialize in different aspects of a problem.
多框架协作: A2A 的主要使用场景是使独立 AI 智能体能够进行通信和协作, 无论其底层框架如何 (例如 ADK、LangChain、CrewAI)。这对于构建复杂多智能体系统至关重要, 在这些系统中, 不同智能体专注于问题的不同方面。
Automated Workflow Orchestration: In enterprise settings, A2A can facilitate complex workflows by enabling agents to delegate and coordinate tasks. For instance, an agent might handle initial data collection, then delegate to another agent for analysis, and finally to a third for report generation, all communicating via the A2A protocol.
自动化工作流编排: 在企业环境中, A2A 可以通过使智能体能够委派和协调任务来促进复杂的工作流。例如, 一个智能体可能负责初始数据收集, 然后委派给另一个智能体进行分析, 最后再委派给第三个智能体生成报告, 所有这些都通过 A2A 协议进行通信。
Dynamic Information Retrieval: Agents can communicate to retrieve and exchange real-time information. A primary agent might request live market data from a specialized "data fetching agent," which then uses external APIs to gather the information and send it back.
动态信息检索: 智能体可以通信以检索和交换实时信息。主智能体可能会向专门的「数据获取智能体」请求实时市场数据, 该智能体随后使用外部 API 收集信息并将其发回。
Hands-On Code Example | 动手代码示例
Let's examine the practical applications of the A2A protocol. The repository at https://github.com/google-a2a/a2a-samples/tree/main/samples provides examples in Java, Go, and Python that illustrate how various agent frameworks, such as LangGraph, CrewAI, Azure AI Foundry, and AG2, can communicate using A2A. All code in this repository is released under the Apache 2.0 license. To further illustrate A2A's core concepts, we will review code excerpts focusing on setting up an A2A Server using an ADK-based agent with Google-authenticated tools.Looking at https://github.com/google-a2a/a2a-samples/blob/main/samples/python/agents/birthday_planner_adk/calendar_agent/adk_agent.py
让我们来研究一下 A2A 协议的实际应用。位于 https://github.com/google-a2a/a2a-samples/tree/main/samples 的代码仓库提供了 Java、Go 和 Python 的示例, 展示了各种智能体框架 (如 LangGraph、CrewAI、 Azure AI Foundry 和 AG2) 如何使用 A2A 进行通信。该仓库中的所有代码均在 Apache 2.0 许可下发布。为了进一步说明 A2A 的核心概念, 我们将回顾一些代码片段, 重点介绍如何使用基于 ADK 的智能体和经过 Google 认证的工具来设置 A2A 服务器。请看 https://github.com/google-a2a/a2a-samples/blob/main/samples/python/agents/birthday_planner_adk/calendar_agent/adk_agent.py
import datetime
from google.adk.agents import LlmAgent # type: ignore[import-untyped]
from google.adk.tools.google_api_tool import CalendarToolset # type: ignore[import-untyped]
async def create_agent(client_id, client_secret) -> LlmAgent:
"""Constructs the ADK agent."""
toolset = CalendarToolset(client_id=client_id, client_secret=client_secret)
return LlmAgent(
model='gemini-2.0-flash-001',
name='calendar_agent',
description="An agent that can help manage a user's calendar",
instruction=f"""
You are an agent that can help manage a user's calendar.
Users will request information about the state of their calendar
or to make changes to their calendar.
Use the provided tools for interacting with the calendar API.
If not specified, assume the calendar the user wants is the 'primary' calendar.
When using the Calendar API tools, use well-formed RFC3339 timestamps.
Today is {datetime.datetime.now()}.
""",
tools=await toolset.get_tools(),
)
This Python code defines an asynchronous function create_agent that constructs an ADK LlmAgent. It begins by initializing a CalendarToolset using the provided client credentials to access the Google Calendar API. Subsequently, an LlmAgent instance is created, configured with a specified Gemini model, a descriptive name, and instructions for managing a user's calendar. The agent is furnished with calendar tools from the CalendarToolset, enabling it to interact with the Calendar API and respond to user queries regarding calendar states or modifications. The agent's instructions dynamically incorporate the current date for temporal context.
这段 Python 代码定义了异步函数 create_agent, 用于构建 ADK LlmAgent。它首先使用提供的客户端凭据初始化 CalendarToolset 以访问 Google Calendar API。随后, 创建 LlmAgent 实例, 配置指定的 Gemini 模型、描述性名称以及管理用户日历的指令。该智能体配备了来自 CalendarToolset 的日历工具, 使其能够与 Calendar API 交互, 并响应用户关于日历状态或修改的查询。智能体的指令动态地包含了当前日期以提供时间上下文。
To illustrate how an agent is constructed, let's examine a key section from the calendar_agent found in the A2A samples on GitHub. The code below shows how the agent is defined with its specific instructions and tools. Please note that only the code required to explain this functionality is shown; you can access the complete file here: https://github.com/a2aproject/a2a-samples/blob/main/samples/python/agents/birthday_planner_adk/calendar_agent/main.py
为了说明如何构建智能体, 让我们看一下 GitHub 上 A2A 示例中 calendar_agent 的关键部分。下面的代码展示了如何使用特定指令和工具定义智能体。请注意, 这里只显示了解释此功能所需的代码; 完整文件可以在此处访问: https://github.com/a2aproject/a2a-samples/blob/main/samples/python/agents/birthday_planner_adk/calendar_agent/main.py
def main(host: str, port: int):
# Verify an API key is set.
# Not required if using Vertex AI APIs.
if os.getenv('GOOGLE_GENAI_USE_VERTEXAI') != 'TRUE' and not os.getenv(
'GOOGLE_API_KEY'
):
raise ValueError(
'GOOGLE_API_KEY environment variable not set and '
'GOOGLE_GENAI_USE_VERTEXAI is not TRUE.'
)
skill = AgentSkill(
id='check_availability',
name='Check Availability',
description="Checks a user's availability for a time using their Google Calendar",
tags=['calendar'],
examples=['Am I free from 10am to 11am tomorrow?'],
)
agent_card = AgentCard(
name='Calendar Agent',
description="An agent that can manage a user's calendar",
url=f'http://{host}:{port}/',
version='1.0.0',
defaultInputModes=['text'],
defaultOutputModes=['text'],
capabilities=AgentCapabilities(streaming=True),
skills=[skill],
)
adk_agent = asyncio.run(create_agent(
client_id=os.getenv('GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID'),
client_secret=os.getenv('GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET'),
))
runner = Runner(
app_name=agent_card.name,
agent=adk_agent,
artifact_service=InMemoryArtifactService(),
session_service=InMemorySessionService(),
memory_service=InMemoryMemoryService(),
)
agent_executor = ADKAgentExecutor(runner, agent_card)
async def handle_auth(request: Request) -> PlainTextResponse:
await agent_executor.on_auth_callback(
str(request.query_params.get('state')), str(request.url)
)
return PlainTextResponse('Authentication successful.')
request_handler = DefaultRequestHandler(
agent_executor=agent_executor, task_store=InMemoryTaskStore()
)
a2a_app = A2AStarletteApplication(
agent_card=agent_card, http_handler=request_handler
)
routes = a2a_app.routes()
routes.append(
Route(
path='/authenticate',
methods=['GET'],
endpoint=handle_auth,
)
)
app = Starlette(routes=routes)
uvicorn.run(app, host=host, port=port)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
This Python code demonstrates setting up an A2A-compliant "Calendar Agent" for checking user availability using Google Calendar. It involves verifying API keys or Vertex AI configurations for authentication purposes. The agent's capabilities, including the "check_availability" skill, are defined within an AgentCard, which also specifies the agent's network address. Subsequently, an ADK agent is created, configured with in-memory services for managing artifacts, sessions, and memory. The code then initializes a Starlette web application, incorporates an authentication callback and the A2A protocol handler, and executes it using Uvicorn to expose the agent via HTTP.
这段 Python 代码演示了如何设置符合 A2A 规范的「日历智能体」, 用于使用 Google 日历检查用户空闲状态。它涉及验证 API 密钥或 Vertex AI 配置以进行身份验证。智能体的能力, 包括 check_availability 技能, 都在 AgentCard 中定义, 该卡片还指定了智能体的网络地址。随后, 创建 ADK 智能体, 并配置了用于管理工件、会话和内存的内存服务。然后, 代码初始化 Starlette Web 应用程序, 集成了身份验证回调和 A2A 协议处理器, 并使用 Uvicorn 启动它, 通过 HTTP 暴露该智能体。
These examples illustrate the process of building an A2A-compliant agent, from defining its capabilities to running it as a web service. By utilizing Agent Cards and ADK, developers can create interoperable AI agents capable of integrating with tools like Google Calendar. This practical approach demonstrates the application of A2A in establishing a multi-agent ecosystem.
这些示例说明了构建符合 A2A 规范智能体的过程, 从定义其能力到将其作为 Web 服务运行。通过利用智能体卡片和 ADK, 开发人员可以创建能够与 Google 日历等工具集成的可互操作 AI 智能体。这种实用方法展示了 A2A 在建立多智能体生态系统中的应用。
Further exploration of A2A is recommended through the code demonstration at https://www.trickle.so/blog/how-to-build-google-a2a-project. Resources available at this link include sample A2A clients and servers in Python and JavaScript, multi-agent web applications, command-line interfaces, and example implementations for various agent frameworks.
建议通过 https://www.trickle.so/blog/how-to-build-google-a2a-project 上的代码演示进一步探索 A2A。该链接提供的资源包括 Python 和 JavaScript 的 A2A 客户端和服务器示例、多智能体 Web 应用程序、命令行界面以及各种智能体框架的实现示例。
At a Glance | 概览
What: Individual AI agents, especially those built on different frameworks, often struggle with complex, multi-faceted problems on their own. The primary challenge is the lack of a common language or protocol that allows them to communicate and collaborate effectively. This isolation prevents the creation of sophisticated systems where multiple specialized agents can combine their unique skills to solve larger tasks. Without a standardized approach, integrating these disparate agents is costly, time-consuming, and hinders the development of more powerful, cohesive AI solutions.
问题: 单个 AI 智能体, 特别是那些基于不同框架构建的智能体, 通常难以独立解决复杂、多方面的问题。主要挑战在于缺乏使这些智能体能够有效沟通和协作的通用语言或协议。智能体间的孤立状态阻碍了复杂系统的创建, 在这些系统中, 多个专业智能体本可以结合其独特技能来解决更大的任务。如果没有标准化方法, 集成这些异构智能体的成本高昂、耗时, 并让更强大、更有凝聚力的 AI 解决方案开发变得困难。
Why: The Inter-Agent Communication (A2A) protocol provides an open, standardized solution for this problem. It is an HTTP-based protocol that enables interoperability, allowing distinct AI agents to coordinate, delegate tasks, and share information seamlessly, regardless of their underlying technology. A core component is the Agent Card, a digital identity file that describes an agent's capabilities, skills, and communication endpoints, facilitating discovery and interaction. A2A defines various interaction mechanisms, including synchronous and asynchronous communication, to support diverse use cases. By creating a universal standard for agent collaboration, A2A fosters a modular and scalable ecosystem for building complex, multi-agent Agentic systems.
解决方案: 智能体间通信 (A2A) 协议为这个问题提供了开放、标准化的解决方案。它是基于 HTTP 的协议, 可实现互操作性, 允许不同 AI 智能体无缝协调、委派任务和共享信息, 而不受其底层技术限制。其核心组件是智能体卡片, 这是描述智能体能力、技能和通信端点的数字身份文件, 便于发现和交互。A2A 定义了各种交互机制, 包括同步和异步通信, 以支持不同的使用场景。通过为智能体协作创建通用标准, A2A 为构建复杂多智能体系统提供了模块化和可扩展的生态系统。
Rule of thumb: Use this pattern when you need to orchestrate collaboration between two or more AI agents, especially if they are built using different frameworks (e.g., Google ADK, LangGraph, CrewAI). It is ideal for building complex, modular applications where specialized agents handle specific parts of a workflow, such as delegating data analysis to one agent and report generation to another. This pattern is also essential when an agent needs to dynamically discover and consume the capabilities of other agents to complete a task.
经验法则: 当需要协调两个或多个 AI 智能体之间的协作时, 尤其是在它们使用不同框架 (例如 Google ADK、LangGraph、CrewAI) 构建的情况下, 请使用此模式。它非常适合构建复杂模块化应用程序, 其中专门的智能体处理工作流的特定部分, 例如将数据分析委派给一个智能体, 将报告生成委派给另一个智能体。当智能体需要动态发现和使用其他智能体的能力来完成任务时, 此模式也至关重要。
Visual summary
可视化摘要
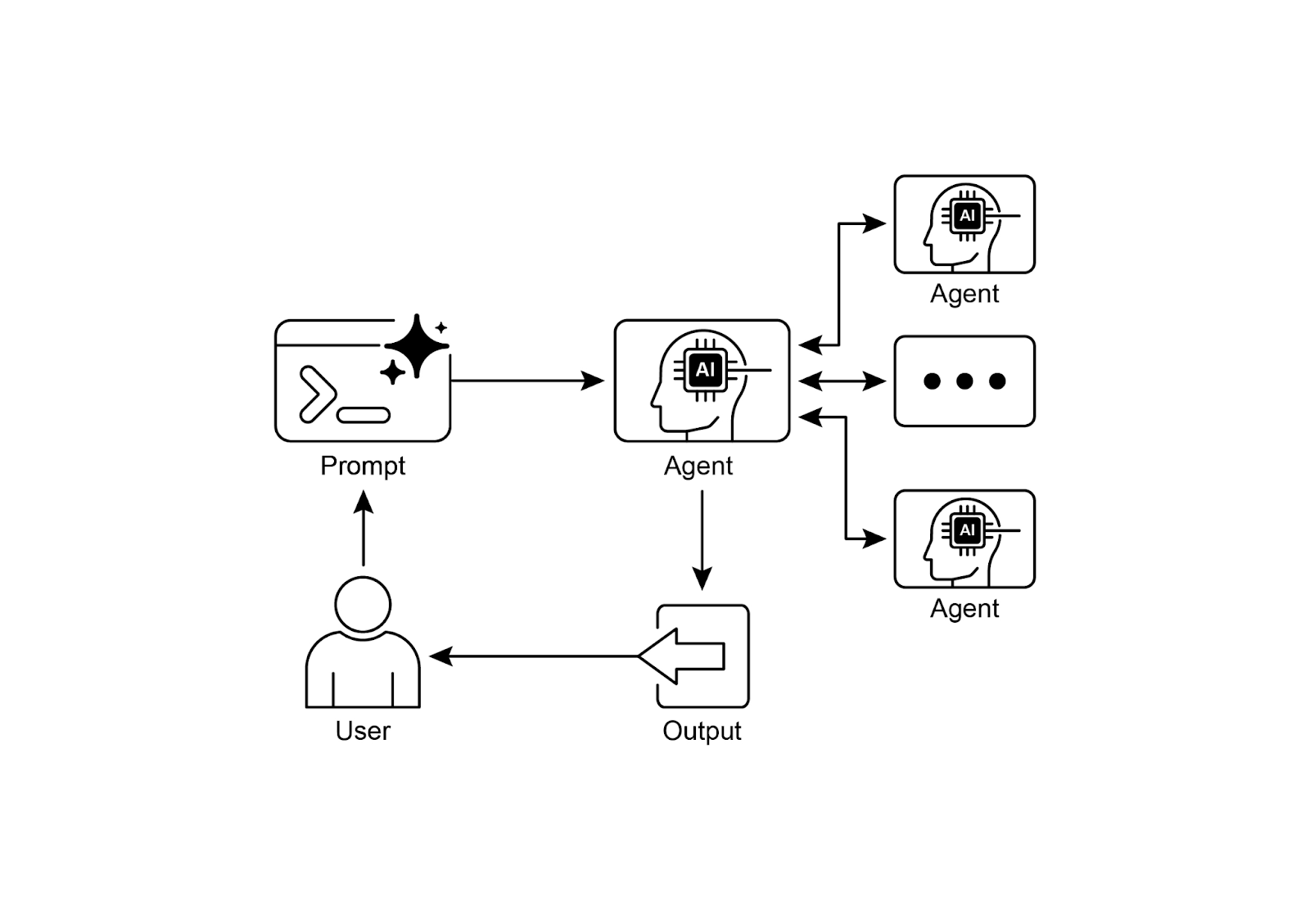 Fig.2: A2A inter-agent communication pattern
Fig.2: A2A inter-agent communication pattern
图 2: A2A 智能体间通信模式
Key Takeaways | 关键要点
Key Takeaways:
关键要点
-
The Google A2A protocol is an open, HTTP-based standard that facilitates communication and collaboration between AI agents built with different frameworks.
-
Google A2A 协议是一个开放的、基于 HTTP 的标准, 它促进了由不同框架构建的 AI 智能体之间的通信和协作。
-
An AgentCard serves as a digital identifier for an agent, allowing for automatic discovery and understanding of its capabilities by other agents.
-
智能体卡片作为智能体的数字标识符, 允许其他智能体自动发现和理解其能力。
-
A2A offers both synchronous request-response interactions (using
tasks/send) and streaming updates (usingtasks/sendSubscribe) to accommodate varying communication needs. -
A2A 提供同步请求-响应交互 (使用
tasks/send) 和流式更新 (使用tasks/sendSubscribe), 以适应不同的通信需求。 -
The protocol supports multi-turn conversations, including an
input-requiredstate, which allows agents to request additional information and maintain context during interactions. -
该协议支持多轮对话, 包括
input-required状态, 允许智能体在交互过程中请求额外信息并保持上下文。 -
A2A encourages a modular architecture where specialized agents can operate independently on different ports, enabling system scalability and distribution.
-
A2A 鼓励采用模块化架构, 其中专门的智能体可以在不同端口上独立运行, 从而实现系统的可扩展性和分布式部署。
-
Tools such as Trickle AI aid in visualizing and tracking A2A communications, which helps developers monitor, debug, and optimize multi-agent systems.
-
像 Trickle AI 这样的工具有助于可视化和跟踪 A2A 通信, 帮助开发人员监控、调试和优化多智能体系统。
-
While A2A is a high-level protocol for managing tasks and workflows between different agents, the Model Context Protocol (MCP) provides a standardized interface for LLMs to interface with external resources
-
A2A 是一个用于管理不同智能体之间任务和工作流的高级协议, 而模型上下文协议 (MCP) 则为 LLM 与外部资源交互提供了一个标准化的接口。
Conclusions | 结论
The Inter-Agent Communication (A2A) protocol establishes a vital, open standard to overcome the inherent isolation of individual AI agents. By providing a common HTTP-based framework, it ensures seamless collaboration and interoperability between agents built on different platforms, such as Google ADK, LangGraph, or CrewAI. A core component is the Agent Card, which serves as a digital identity, clearly defining an agent's capabilities and enabling dynamic discovery by other agents. The protocol's flexibility supports various interaction patterns, including synchronous requests, asynchronous polling, and real-time streaming, catering to a wide range of application needs. This enables the creation of modular and scalable architectures where specialized agents can be combined to orchestrate complex automated workflows. Security is a fundamental aspect, with built-in mechanisms like mTLS and explicit authentication requirements to protect communications. While complementing other standards like MCP, A2A's unique focus is on the high-level coordination and task delegation between agents. The strong backing from major technology companies and the availability of practical implementations highlight its growing importance. This protocol paves the way for developers to build more sophisticated, distributed, and intelligent multi-agent systems. Ultimately, A2A is a foundational pillar for fostering an innovative and interoperable ecosystem of collaborative AI.
智能体间通信 (A2A) 协议建立了至关重要的开放标准, 克服了单个 AI 智能体固有的孤立性。通过提供通用的基于 HTTP 的框架, 它确保了在不同平台 (如 Google ADK、LangGraph 或 CrewAI) 上构建的智能体之间的无缝协作和互操作性。其核心组件是智能体卡片, 它作为数字身份, 清晰地定义了智能体的能力, 并使其他智能体能够动态发现。该协议的灵活性支持各种交互模式, 包括同步请求、异步轮询和实时流式传输, 满足了广泛的应用需求。这使得创建模块化和可扩展的架构成为可能, 其中专门的智能体可以组合起来编排复杂的自动化工作流。安全性是最基础的能力, 内置了 mTLS 和明确的身份验证要求等机制来保护通信。虽然 A2A 与 MCP 等其他标准互补, 但其独特的重点在于智能体之间的高层协调和任务委派。来自主流技术公司的强大支持和实际实现的可用性凸显了其日益增长的重要性。该协议为开发人员构建更复杂、分布式和智能的多智能体系统铺平了道路。最终, A2A 是促进协作式 AI 的创新和互操作生态系统的基础支柱。
References | 参考文献
- Chen, B. (2025, April 22). How to Build Your First Google A2A Project: A Step-by-Step Tutorial. Trickle.so Blog. https://www.trickle.so/blog/how-to-build-google-a2a-project
- Google A2A GitHub Repository. https://github.com/google-a2a/A2A
- Google Agent Development Kit (ADK) https://google.github.io/adk-docs/
- Getting Started with Agent-to-Agent (A2A) Protocol: https://codelabs.developers.google.com/intro-a2a-purchasing-concierge#0
- Google Agent Discovery - https://a2a-protocol.org/latest/
- Communication between different AI frameworks such as LangGraph, CrewAI, and Google ADK https://www.trickle.so/blog/how-to-build-google-a2a-project
- Designing Collaborative Multi-Agent Systems with the A2A Protocol https://www.oreilly.com/radar/designing-collaborative-multi-agent-systems-with-the-a2a-protocol/