Chapter 06: Planning
Chapter 6: Planning | 第六章:规划
Intelligent behavior often involves more than just reacting to the immediate input. It requires foresight, breaking down complex tasks into smaller, manageable steps, and strategizing how to achieve a desired outcome. This is where the Planning pattern comes into play. At its core, planning is the ability for an agent or a system of agents to formulate a sequence of actions to move from an initial state towards a goal state.
智能行为远不止对眼前输入作出反应。它需要前瞻性,需要把复杂任务拆解为更小且可管理的步骤,并制定实现预期结果的策略。这正是规划模式发挥作用之处。其核心在于:智能体(或智能体系统)能够制定一系列行动,使系统从初始状态迈向目标状态。
Planning Pattern Overview | 规划模式概览
In the context of AI, it's helpful to think of a planning agent as a specialist to whom you delegate a complex goal. When you ask it to "organize a team offsite," you are defining the what—the objective and its constraints—but not the how. The agent's core task is to autonomously chart a course to that goal. It must first understand the initial state (e.g., budget, number of participants, desired dates) and the goal state (a successfully booked offsite), and then discover the optimal sequence of actions to connect them. The plan is not known in advance; it is created in response to the request.
在 AI 的语境下,把规划智能体看作可以委派复杂目标的专家会更容易理解。当你请它「组织团队外出活动」时,你声明了需要它「做什么」——目标及其约束条件——而不是定义「如何做」。智能体的核心任务是自主规划通往该目标的路径:首先是要弄清楚当前状况(如预算、人数、日期)和目标状态(如已经成功预订的外出活动),然后找出将两者衔接起来的最佳行动步骤。而且这个计划并非预先存在的,而是根据请求即时生成的。
A hallmark of this process is adaptability. An initial plan is merely a starting point, not a rigid script. The agent's real power is its ability to incorporate new information and steer the project around obstacles. For instance, if the preferred venue becomes unavailable or a chosen caterer is fully booked, a capable agent doesn't simply fail. It adapts. It registers the new constraint, re-evaluates its options, and formulates a new plan, perhaps by suggesting alternative venues or dates.
这一过程的关键是灵活应变。初步计划只是出发点,而非僵硬的指令。智能体的真正能力在于接纳新信息,并在遇到阻碍时调整路线。比如,当首选场地临时无法使用或选定的餐饮服务已约满时,有能力的智能体不会就此终止,而是会根据新的约束重新评估可选方案,制定替代计划,如建议更换场地或调整日期。
However, it is crucial to recognize the trade-off between flexibility and predictability. Dynamic planning is a specific tool, not a universal solution. When a problem's solution is already well-understood and repeatable, constraining the agent to a predetermined, fixed workflow is more effective. This approach limits the agent's autonomy to reduce uncertainty and the risk of unpredictable behavior, guaranteeing a reliable and consistent outcome. Therefore, the decision to use a planning agent versus a simple task-execution agent hinges on a single question: does the "how" need to be discovered, or is it already known?
然而,我们必须认识到灵活性与可预测性之间的权衡。动态规划是一个专用工具,而非万能解。当问题的解决方法已经清楚且可以重复时,让系统遵循预先设定的固定流程通常更有效。通过限制系统的自主权,可以降低不确定性和不可预测行为的风险,从而确保结果更加可靠一致。因此,是否采用规划型智能体还是简单的任务处理型智能体,关键点在于:「如何做」的方案是否需要探索,还是已经明确了?
Practical Applications & Use Cases | 实际应用场景
The Planning pattern is a core computational process in autonomous systems, enabling an agent to synthesize a sequence of actions to achieve a specified goal, particularly within dynamic or complex environments. This process transforms a high-level objective into a structured plan composed of discrete, executable steps.
规划是自主系统的核心计算过程之一,它使智能体能够在动态或复杂的环境中,设计出一连串动作来实现特定目标。该过程把高层次的目标转化为由若干可执行的具体步骤组成的结构化计划。
In domains such as procedural task automation, planning is used to orchestrate complex workflows. For example, a business process like onboarding a new employee can be decomposed into a directed sequence of sub-tasks, such as creating system accounts, assigning training modules, and coordinating with different departments. The agent generates a plan to execute these steps in a logical order, invoking necessary tools or interacting with various systems to manage dependencies.
在流程自动化等领域,规划用于编排复杂工作流。例如,新员工入职这样的业务流程可以分解成一系列有序的子任务,如创建系统账户、分配培训课程、与各部门协调等。智能体会制定计划,并按逻辑顺序执行这些步骤,调用必要的工具或与各类系统交互,以处理各项依赖关系。
Within robotics and autonomous navigation, planning is fundamental for state-space traversal. A system, whether a physical robot or a virtual entity, must generate a path or sequence of actions to transition from an initial state to a goal state. This involves optimizing for metrics such as time or energy consumption while adhering to environmental constraints, like avoiding obstacles or following traffic regulations.
在机器人与自主导航中,规划是进行状态空间遍历的核心。无论是实体机器人还是虚拟主体,系统都需要生成路径或动作序列,从起始状态到达目标状态。这个过程要在遵守环境约束(如避障或遵守交通法规)的前提下,优化时间、能耗等指标。
This pattern is also critical for structured information synthesis. When tasked with generating a complex output like a research report, an agent can formulate a plan that includes distinct phases for information gathering, data summarization, content structuring, and iterative refinement. Similarly, in customer support scenarios involving multi-step problem resolution, an agent can create and follow a systematic plan for diagnosis, solution implementation, and escalation.
这种模式对结构化的信息整合也至关重要。当任务需要生成研究报告等复杂输出时,智能体可以制定包含信息收集、数据归纳、内容结构化与迭代打磨等阶段的计划。在涉及多步骤问题解决的客户支持场景中,智能体也能制定并执行一套系统化流程来进行诊断、实施解决方案并在必要时升级处理。
In essence, the Planning pattern allows an agent to move beyond simple, reactive actions to goal-oriented behavior. It provides the logical framework necessary to solve problems that require a coherent sequence of interdependent operations.
本质上,规划模式使智能体不再局限于简单的被动反应,而是能够以目标为导向地行动。它为解决那些需要一系列相互关联步骤才能完成的问题,提供了必要的逻辑框架。
Hands-on code (Crew AI) | 实战代码:使用 Crew AI
The following section will demonstrate an implementation of the Planner pattern using the Crew AI framework. This pattern involves an agent that first formulates a multi-step plan to address a complex query and then executes that plan sequentially.
接下来我们将演示如何使用 CrewAI 框架实现规划模式。该模式中,智能体先制定多步骤的计划来解决复杂问题,然后按步骤依次执行该计划。
import os
from dotenv import load_dotenv
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew, Process
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
# Load environment variables from .env file for security
# 从 .env 文件加载环境变量(如 OPENAI_API_KEY)
load_dotenv()
# 1. Explicitly define the language model for clarity
# 明确指定使用的模型
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4-turbo")
# 2. Define a clear and focused agent
# 定义一个目标明确且聚焦的智能体
planner_writer_agent = Agent(
role='Article Planner and Writer',
goal='Plan and then write a concise, engaging summary on a specified topic.',
backstory=(
'You are an expert technical writer and content strategist. '
'Your strength lies in creating a clear, actionable plan before writing, '
'ensuring the final summary is both informative and easy to digest.'
),
verbose=True,
allow_delegation=False,
llm=llm # Assign the specific LLM to the agent
)
# 3. Define a task with a more structured and specific expected output
# 定义一个更结构化且输出明确的任务
topic = "The importance of Reinforcement Learning in AI"
high_level_task = Task(
description=(
f"1. Create a bullet-point plan for a summary on the topic: '{topic}'.\n"
f"2. Write the summary based on your plan, keeping it around 200 words."
),
expected_output=(
"A final report containing two distinct sections:\n\n"
"### Plan\n"
"- A bulleted list outlining the main points of the summary.\n\n"
"### Summary\n"
"- A concise and well-structured summary of the topic."
),
agent=planner_writer_agent,
)
# Create the crew with a clear process
# 创建一个 Crew 实例来执行任务
crew = Crew(
agents=[planner_writer_agent],
tasks=[high_level_task],
process=Process.sequential,
)
# Execute the task
# 开始执行
print("## Running the planning and writing task ##")
result = crew.kickoff()
print("\n\n---\n## Task Result ##\n---")
print(result)
This code uses the CrewAI library to create an AI agent that plans and writes a summary on a given topic. It starts by importing necessary libraries, including Crew.ai and langchain_openai, and loading environment variables from a .env file. A ChatOpenAI language model is explicitly defined for use with the agent. An Agent named planner_writer_agent is created with a specific role and goal: to plan and then write a concise summary. The agent's backstory emphasizes its expertise in planning and technical writing. A Task is defined with a clear description to first create a plan and then write a summary on the topic "The importance of Reinforcement Learning in AI", with a specific format for the expected output. A Crew is assembled with the agent and task, set to process them sequentially. Finally, the crew.kickoff() method is called to execute the defined task and the result is printed.
此代码使用 CrewAI 库创建一个在给定主题上进行规划并撰写摘要的 AI 智能体。
代码先导入依赖的库,包括 crewai 与 langchain_openai,并从 .env 文件加载环境变量。随后为智能体指定并使用了一个 ChatOpenAI 语言模型。接着创建名为 planner_writer_agent 的智能体,设定其角色和目标:先制定计划、然后撰写简洁的摘要,并在背景介绍中强调在规划与技术写作方面的专长。随后定义一个任务:明确要求先生成计划再就「强化学习在 AI 中的重要性」这个主题撰写摘要,并对输出格式作出具体要求。最后使用该智能体与任务构建 Crew 实例,设置为顺序处理,并调用 crew.kickoff() 启动任务并打印结果。
Google DeepResearch | Google 深度研究
Google Gemini DeepResearch (see Fig.1) is an agent-based system designed for autonomous information retrieval and synthesis. It functions through a multi-step agentic pipeline that dynamically and iteratively queries Google Search to systematically explore complex topics. The system is engineered to process a large corpus of web-based sources, evaluate the collected data for relevance and knowledge gaps, and perform subsequent searches to address them. The final output consolidates the vetted information into a structured, multi-page summary with citations to the original sources.
Google Gemini 深度研究(Google Gemini DeepResearch,见图 1)是一个面向自主信息检索与整合的智能体系统。它通过一个多步骤、动态迭代的智能体流程调用 Google 搜索引擎,系统性地探索复杂主题。该系统能够处理大量网络来源,评估所收集数据的相关性与知识缺口,并发起后续搜索来弥补这些空白。最终产出是经过筛选并带有引用来源的结构化多页摘要。
Expanding on this, the system's operation is not a single query-response event but a managed, long-running process. It begins by deconstructing a user's prompt into a multi-point research plan (see Fig. 1), which is then presented to the user for review and modification. This allows for a collaborative shaping of the research trajectory before execution. Once the plan is approved, the agentic pipeline initiates its iterative search-and-analysis loop. This involves more than just executing a series of predefined searches; the agent dynamically formulates and refines its queries based on the information it gathers, actively identifying knowledge gaps, corroborating data points, and resolving discrepancies.
进一步来说,系统并非一次性的问答事件,而是受控的、持续运行的过程。它会先把用户的提示拆解成多个要点的研究计划(见图 1),再呈现给用户审阅与修改,以便在开始执行前共同确定研究方向。一旦计划获批,智能体便会开启循环的搜索与分析过程。这个过程并非简单地执行预设搜索,而是根据获取到的信息不断生成和调整查询,主动发现知识盲点、核对数据并解决冲突。
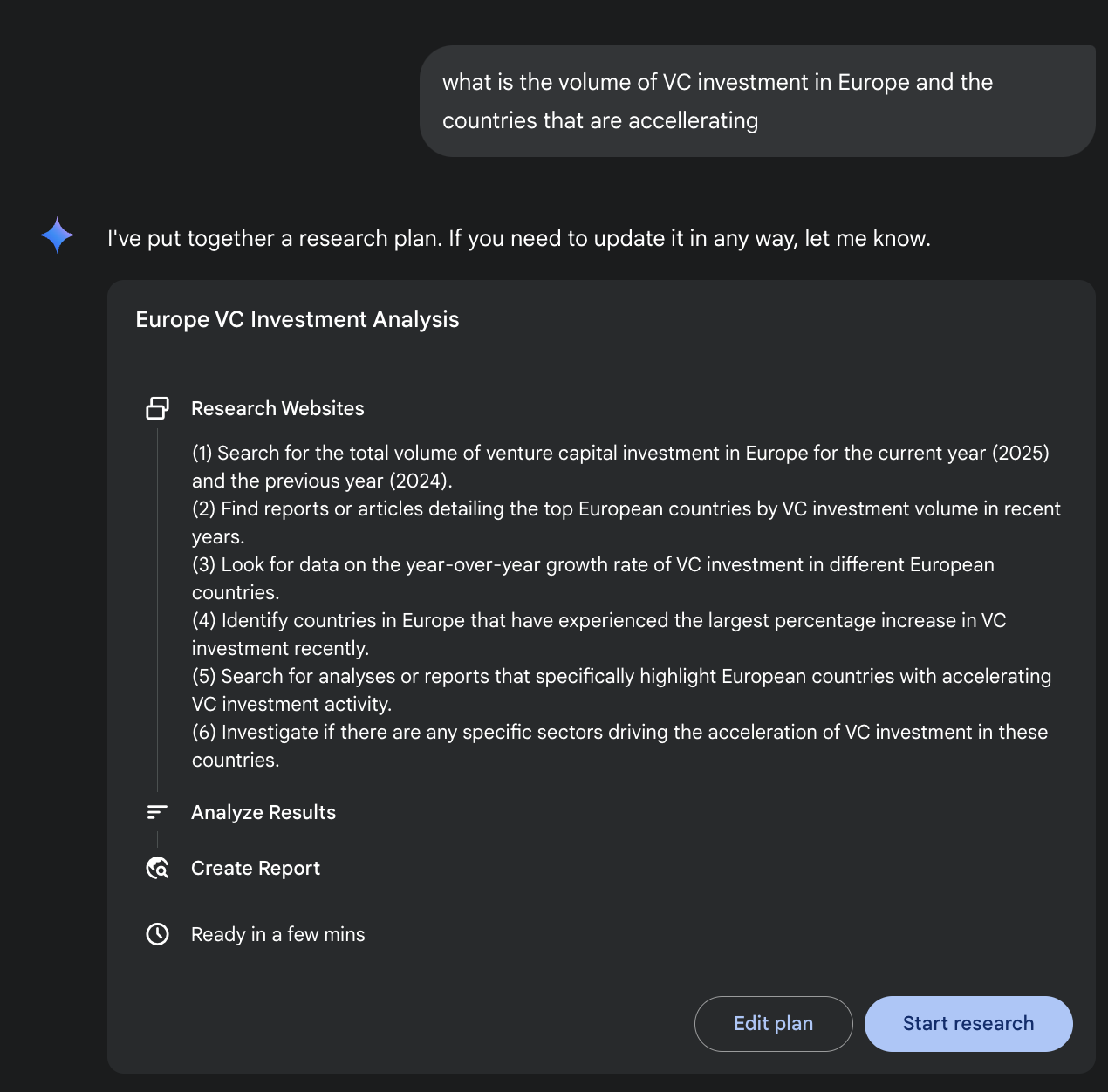
Fig. 1: Google Deep Research agent generating an execution plan for using Google Search as a tool.
图 1:Google 深入研究智能体使用 Google 搜索引擎作为工具,生成详细的执行计划。
A key architectural component is the system's ability to manage this process asynchronously. This design ensures that the investigation, which can involve analyzing hundreds of sources, is resilient to single-point failures and allows the user to disengage and be notified upon completion. The system can also integrate user-provided documents, combining information from private sources with its web-based research. The final output is not merely a concatenated list of findings but a structured, multi-page report. During the synthesis phase, the model performs a critical evaluation of the collected information, identifying major themes and organizing the content into a coherent narrative with logical sections. The report is designed to be interactive, often including features like an audio overview, charts, and links to the original cited sources, allowing for verification and further exploration by the user. In addition to the synthesized results, the model explicitly returns the full list of sources it searched and consulted (see Fig.2). These are presented as citations, providing complete transparency and direct access to the primary information. This entire process transforms a simple query into a comprehensive, synthesized body of knowledge.
一个关键的架构要点是系统对整个流程的异步管理能力。这样的设计使得可能涉及数百个来源的研究具备抵御单点故障的能力,并允许用户中途离开,待任务完成后再收到通知。系统还能整合用户提供的文档,把私有资料和网络搜索到的信息相结合。最终产出不是简单堆砌的要点列表,而是结构化的多页报告。在整合阶段,模型会对收集到的信息进行严格评估,提炼主要主题并按逻辑分成章节,形成连贯的叙述。报告通常是交互式的,如音频简介、图表及指向原始引用来源的链接,便于用户核查和进一步探索。除整合后的结论外,模型还会明确返回其搜索与参考的完整来源清单(见图 2),以引用的形式呈现,确保透明并可直接访问原始资料。整个过程把一次简单的查询转化为全面且系统化的知识成果。
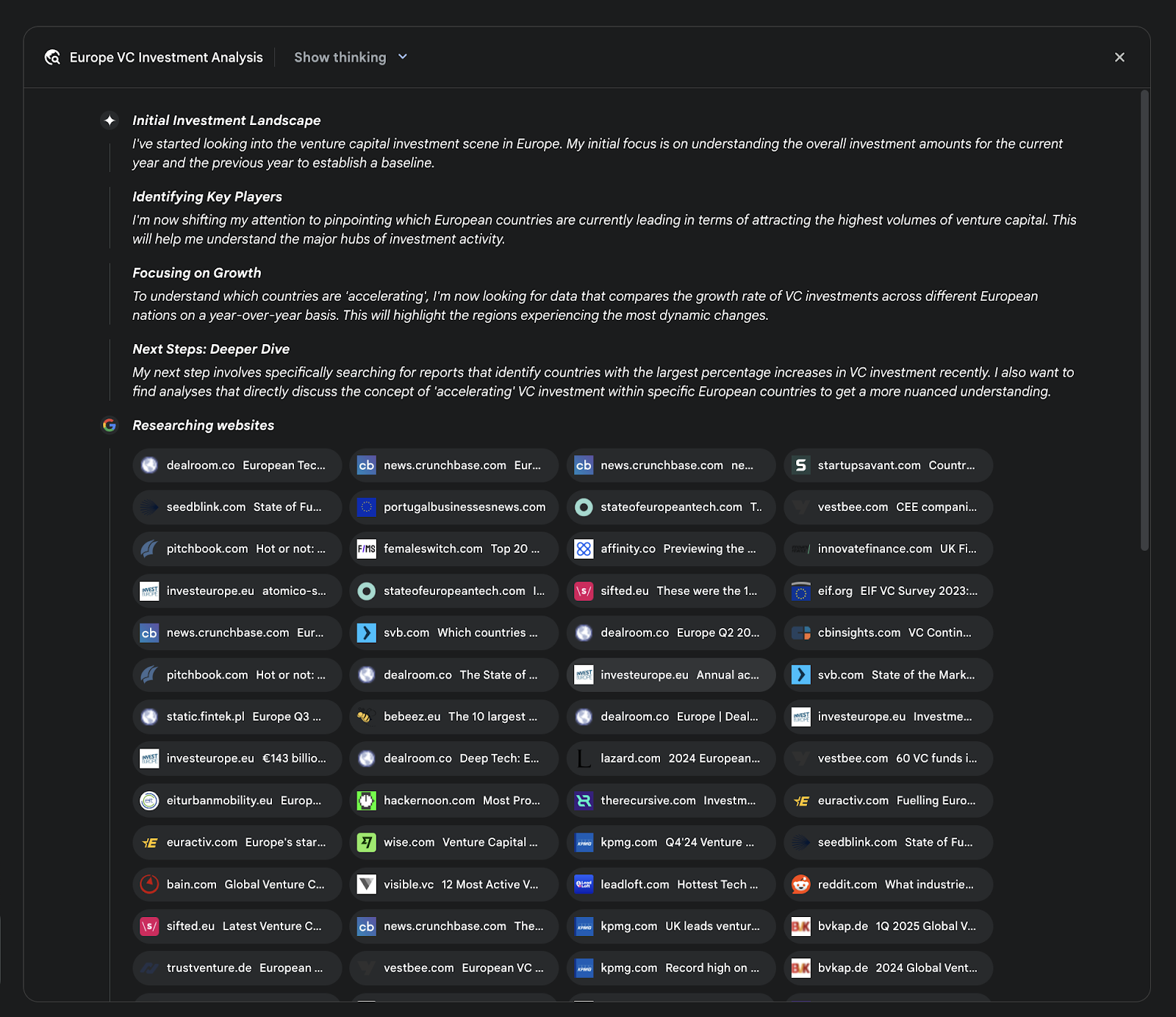
Fig. 2: An example of Deep Research plan being executed, resulting in Google Search being used as a tool to search various web sources.
图 2:一个深入研究计划执行示例,展示了使用 Google 搜索作为工具来检索各类网络来源的信息。
By mitigating the substantial time and resource investment required for manual data acquisition and synthesis, Gemini DeepResearch provides a more structured and exhaustive method for information discovery. The system's value is particularly evident in complex, multi-faceted research tasks across various domains.
通过减少手动数据获取和整合数据所需的大量时间和资源投入,Gemini 深度研究为信息发现提供了更结构化、更全面的方法。在各类复杂、多维的研究任务中,这一系统的价值尤为明显。
For instance, in competitive analysis, the agent can be directed to systematically gather and collate data on market trends, competitor product specifications, public sentiment from diverse online sources, and marketing strategies. This automated process replaces the laborious task of manually tracking multiple competitors, allowing analysts to focus on higher-order strategic interpretation rather than data collection (see Fig. 3).
例如,在进行竞争分析时,可以让智能体系统有条不紊地收集并汇总市场趋势、竞争对手产品规格、来自不同渠道的公众舆情以及营销策略等信息。这个自动化流程替代了手动跟踪多个竞争对手的繁琐工作,使分析师能把精力放在更高层次的战略解读上,而不是耗费在数据采集上(见图 3)。
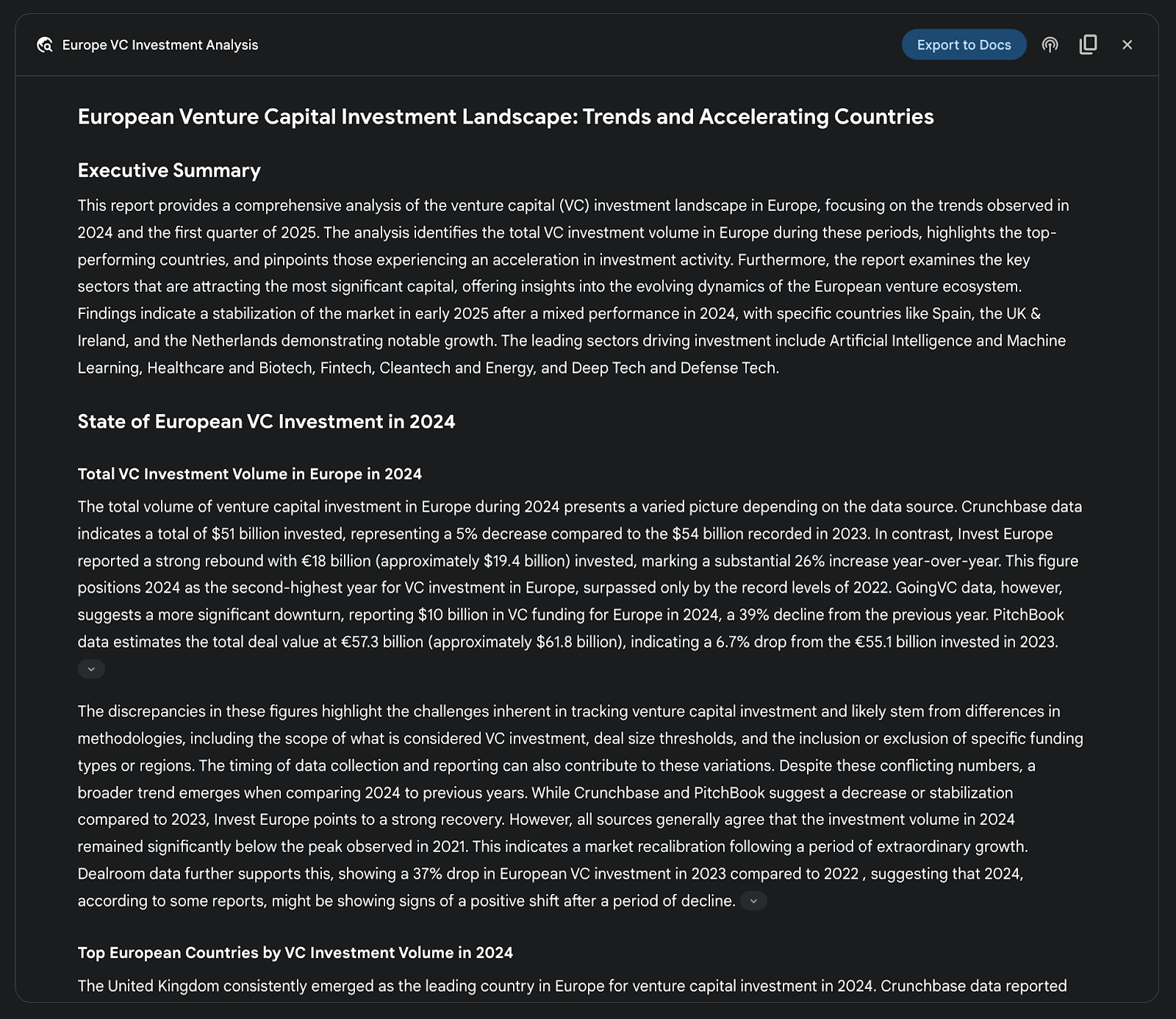
Fig. 3: Final output generated by the Google Deep Research agent, analyzing on our behalf sources obtained using Google Search as a tool.
图 3:Google 深度研究智能体生成的最终结果,基于 Google 搜索获取的资料进行分析。
Similarly, in academic exploration, the system serves as a powerful tool for conducting extensive literature reviews. It can identify and summarize foundational papers, trace the development of concepts across numerous publications, and map out emerging research fronts within a specific field, thereby accelerating the initial and most time-consuming phase of academic inquiry.
同样在学术研究中,该系统也是进行大规模文献综述的有力工具。它可以识别并概括重要论文,梳理概念在多篇文献中的演变轨迹,并勾勒出某一领域的新兴研究方向,从而大大加快学术研究中最初且通常最耗时的阶段。
The efficiency of this approach stems from the automation of the iterative search-and-filter cycle, which is a core bottleneck in manual research. Comprehensiveness is achieved by the system's capacity to process a larger volume and variety of information sources than is typically feasible for a human researcher within a comparable timeframe. This broader scope of analysis helps to reduce the potential for selection bias and increases the likelihood of uncovering less obvious but potentially critical information, leading to a more robust and well-supported understanding of the subject matter.
这种方法之所以高效,是因为它将反复的搜索与筛选过程自动化了,而这正是手动研究的主要瓶颈。系统能在与人类研究者同样多的时间内处理更多、类型更丰富的信息来源,从而实现更全面的覆盖。更广的分析范围还有助于降低选择性偏差的风险,并更容易发现那些不太显眼但可能至关重要的信息,从而得出更可靠、更有依据的结论。
OpenAI Deep Research API | OpenAI 深度研究接口
The OpenAI Deep Research API is a specialized tool designed to automate complex research tasks. It utilizes an advanced, agentic model that can independently reason, plan, and synthesize information from real-world sources. Unlike a simple Q&A model, it takes a high-level query and autonomously breaks it down into sub-questions, performs web searches using its built-in tools, and delivers a structured, citation-rich final report. The API provides direct programmatic access to this entire process, using at the time of writing models like o3-deep-research-2025-06-26 for high-quality synthesis and the faster o4-mini-deep-research-2025-06-26 for latency-sensitive application
OpenAI 深度研究接口(OpenAI Deep Research API)是一款专为自动化复杂研究任务而设计的工具。它利用高级智能体模型,能够独立推理、规划,并从真实世界来源整合信息。不同于简单的问答模型,它接收高层次的问题并自主拆解为若干子问题,借助内置工具进行网络搜索,最终给出结构化且带有引用的报告。通过该接口可以用编程的方式控制整个流程。撰写本书时可使用 o3-deep-research-2025-06-26 模型生成高质量的调研内容,而 o4-mini-deep-research-2025-06-26 模型则可用于对延迟更敏感的场景。
The Deep Research API is useful because it automates what would otherwise be hours of manual research, delivering professional-grade, data-driven reports suitable for informing business strategy, investment decisions, or policy recommendations. Its key benefits include:
深度研究接口很有用,因为它能将本需数小时人工调研的工作自动化,产出用于商业战略、投资决策或政策建议的专业级、数据驱动的报告。其主要优势包括:
-
Structured, Cited Output: It produces well-organized reports with inline citations linked to source metadata, ensuring claims are verifiable and data-backed.
结构化、有引用的输出:它生成结构清晰的报告,在文中插入与来源关联的引用,从而使结论可核查并有数据支撑。
-
Transparency: Unlike the abstracted process in ChatGPT, the API exposes all intermediate steps, including the agent's reasoning, the specific web search queries it executed, and any code it ran. This allows for detailed debugging, analysis, and a deeper understanding of how the final answer was constructed.
透明度:与 ChatGPT 中的抽象过程不同,该接口会展示所有中间步骤,包括智能体的推理、它执行的具体网络搜索查询以及运行的任何代码。这使得对答案的生成过程可以进行更细致的调试与分析,并更清楚地了解最终结果是如何形成的。
-
Extensibility: It supports the Model Context Protocol (MCP), enabling developers to connect the agent to private knowledge bases and internal data sources, blending public web research with proprietary information.
可扩展性:它支持模型上下文协议(MCP),使开发者能够将智能体连接到私有知识库和内部数据源,将公共网络研究与专有信息结合。
To use the API, you send a request to the client.responses.create endpoint, specifying a model, an input prompt, and the tools the agent can use. The input typically includes a system_message that defines the agent's persona and desired output format, along with the user_query. You must also include the web_search_preview tool and can optionally add others like code_interpreter or custom MCP tools (see Chapter 10) for internal data.
要使用该接口,你需要向 client.responses.create 端点发送请求,指定模型、输入提示词和智能体可以使用的工具。输入通常包括定义智能体角色和期望输出格式的 system_message,以及 user_query。还必须包含 web_search_preview 工具,并添加其他可选工具,如 code_interpreter 或自定义 MCP 工具(见第 10 章)用于处理内部数据。
from openai import OpenAI
# Initialize the client with your API key
# 使用你的 API 密钥初始化 OpenAI 客户端
client = OpenAI(api_key="YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY")
# Define the agent's role and the user's research question
# 定义智能体的角色和用户的研究问题
system_message = """You are a professional researcher preparing a structured, data-driven report.
Focus on data-rich insights, use reliable sources, and include inline citations."""
user_query = "Research the economic impact of semaglutide on global healthcare systems."
# Create the Deep Research API call
# 调用深度研究 API
response = client.responses.create(
model="o3-deep-research-2025-06-26",
input=[
{
"role": "developer",
"content": [{"type": "input_text", "text": system_message}]
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": [{"type": "input_text", "text": user_query}]
}
],
reasoning={"summary": "auto"},
tools=[{"type": "web_search_preview"}]
)
# Access and print the final report from the response
# 访问响应并将其中的最终报告提取并打印出来
final_report = response.output[-1].content[0].text
print(final_report)
# --- ACCESS INLINE CITATIONS AND METADATA ---
# 访问内联引用和元数据
print("--- CITATIONS ---")
annotations = response.output[-1].content[0].annotations
if not annotations:
print("No annotations found in the report.")
else:
for i, citation in enumerate(annotations):
# The text span the citation refers to
cited_text = final_report[citation.start_index:citation.end_index]
print(f"Citation {i+1}:")
print(f" Cited Text: {cited_text}")
print(f" Title: {citation.title}")
print(f" URL: {citation.url}")
print(f" Location: chars {citation.start_index}–{citation.end_index}")
print("\n" + "="*50 + "\n")
# --- INSPECT INTERMEDIATE STEPS ---
# 检查中间步骤
print("--- INTERMEDIATE STEPS ---")
# 1. Reasoning Steps: Internal plans and summaries generated by the model.
# 1. 推理步骤:模型生成的内部计划和总结内容。
try:
reasoning_step = next(item for item in response.output if item.type == "reasoning")
print("\n[Found a Reasoning Step]")
for summary_part in reasoning_step.summary:
print(f" - {summary_part.text}")
except StopIteration:
print("\nNo reasoning steps found.")
# 2. Web Search Calls: The exact search queries the agent executed.
# 2. 网络搜索调用:智能体执行的具体搜索操作。
try:
search_step = next(item for item in response.output if item.type == "web_search_call")
print("\n[Found a Web Search Call]")
print(f" Query Executed: '{search_step.action['query']}'")
print(f" Status: {search_step.status}")
except StopIteration:
print("\nNo web search steps found.")
# 3. Code Execution: Any code run by the agent using the code interpreter.
# 3. 代码执行:智能体使用代码解释器运行的所有代码。
try:
code_step = next(item for item in response.output if item.type == "code_interpreter_call")
print("\n[Found a Code Execution Step]")
print(" Code Input:")
print(f" ```python\n{code_step.input}\n ```")
print(" Code Output:")
print(f" {code_step.output}")
except StopIteration:
print("\nNo code execution steps found.")
This code snippet utilizes the OpenAI API to perform a "Deep Research" task. It starts by initializing the OpenAI client with your API key, which is crucial for authentication. Then, it defines the role of the AI agent as a professional researcher and sets the user's research question about the economic impact of semaglutide. The code constructs an API call to the o3-deep-research-2025-06-26 model, providing the defined system message and user query as input. It also requests an automatic summary of the reasoning and enables web search capabilities. After making the API call, it extracts and prints the final generated report.
以上代码演示了如何使用 OpenAI 接口来执行深度研究。首先需要使用你的 API Key 初始化 OpenAI 客户端,用于身份验证。随后定义 AI 智能体的角色(专业研究员),并设置「关于司美格鲁肽对全球医疗体系经济影响」的研究话题。接着向 o3-deep-research-2025-06-26 模型发起接口请求,传入预设的系统消息和用户查询,同时请求自动生成推理摘要并启用网络搜索功能。完成调用后,代码会提取并打印最终生成的报告。
Subsequently, it attempts to access and display inline citations and metadata from the report's annotations, including the cited text, title, URL, and location within the report. Finally, it inspects and prints details about the intermediate steps the model took, such as reasoning steps, web search calls (including the query executed), and any code execution steps if a code interpreter was used.
随后,代码会从报告的注释中读取并展示内联引用与元数据,包括被引用的文本、标题、链接以及在报告中出现的位置。最后,它还会检查并打印模型执行过的中间步骤的细节,如推理步骤、网络搜索调用(含执行的查询)以及代码执行步骤。
At a Glance | 要点速览
What: Complex problems often cannot be solved with a single action and require foresight to achieve a desired outcome. Without a structured approach, an agentic system struggles to handle multifaceted requests that involve multiple steps and dependencies. This makes it difficult to break down high-level objectives into a manageable series of smaller, executable tasks. Consequently, the system fails to strategize effectively, leading to incomplete or incorrect results when faced with intricate goals.
问题所在:复杂问题往往不能靠一次操作解决,需要提前规划才能达成目标。如果没有结构化的方法,智能体系统就难以处理包含多个步骤和相互依赖的任务,也难以把高层次的目标拆解成可管理的、可执行的小任务。结果就是:面对复杂目标时难以有效制定策略,产出不完整或错误的结论。
Why: The Planning pattern offers a standardized solution by having an agentic system first create a coherent plan to address a goal. It involves decomposing a high-level objective into a sequence of smaller, actionable steps or sub-goals. This allows the system to manage complex workflows, orchestrate various tools, and handle dependencies in a logical order. LLMs are particularly well-suited for this, as they can generate plausible and effective plans based on their vast training data. This structured approach transforms a simple reactive agent into a strategic executor that can proactively work towards a complex objective and even adapt its plan if necessary.
解决之道:规划模式的做法是先由智能体制定一个清晰的计划,再据此推进目标。它将高层次的目标拆解为一系列更小、可执行的步骤或子目标,使系统能够有条不紊地管理复杂工作流、编排各类工具,并按逻辑顺序处理依赖关系。大语言模型尤其擅长此类任务,能够基于其广泛的训练数据生成合理、有效的计划。借助这种结构化方法,可以把简单的被动式智能体变成主动的战略执行者,能够实现复杂目标并在必要时灵活调整计划。
Rule of thumb: Use this pattern when a user's request is too complex to be handled by a single action or tool. It is ideal for automating multi-step processes, such as generating a detailed research report, onboarding a new employee, or executing a competitive analysis. Apply the Planning pattern whenever a task requires a sequence of interdependent operations to reach a final, synthesized outcome.
经验法则:当用户请求复杂到无法由单一动作或工具完成时,应采用此模式。它适用于自动化多步骤流程,例如生成详尽的研究报告、办理新员工入职或开展竞品分析。凡是任务需要通过一系列相互依赖的操作才能得到最终综合性结果的场景,都应考虑使用规划模式。
Visual summary: | 可视化总结:

Fig.4; Planning design pattern
图 4:规划模式
Key Takeaways | 核心要点
-
Planning enables agents to break down complex goals into actionable, sequential steps.
规划使智能体能够把复杂目标拆解为一系列可按顺序执行的具体步骤,从而更有效地完成任务。
-
It is essential for handling multi-step tasks, workflow automation, and navigating complex environments.
它对于处理多步骤任务、实现工作流程自动化以及在复杂环境中导航等场景至关重要。
-
LLMs can perform planning by generating step-by-step approaches based on task descriptions.
大语言模型可根据任务描述生成多步骤的方案,从而实现对任务的规划与执行。
-
Explicitly prompting or designing tasks to require planning steps encourages this behavior in agent frameworks.
通过明确的提示词或在任务设计中要求分解出规划的步骤,可以促使智能体框架产生这种规划行为。
-
Google Deep Research is an agent analyzing on our behalf sources obtained using Google Search as a tool. It reflects, plans, and executes.
Google 深度研究会把 Google 搜索引擎作为工具来代替我们检索与分析来源,具备反思、规划与执行能力。
Conclusion | 结语
In conclusion, the Planning pattern is a foundational component that elevates agentic systems from simple reactive responders to strategic, goal-oriented executors. Modern large language models provide the core capability for this, autonomously decomposing high-level objectives into coherent, actionable steps. This pattern scales from straightforward, sequential task execution, as demonstrated by the CrewAI agent creating and following a writing plan, to more complex and dynamic systems. The Google DeepResearch agent exemplifies this advanced application, creating iterative research plans that adapt and evolve based on continuous information gathering. Ultimately, planning provides the essential bridge between human intent and automated execution for complex problems. By structuring a problem-solving approach, this pattern enables agents to manage intricate workflows and deliver comprehensive, synthesized results.
总之,规划模式是把智能体系统从简单的被动响应者,提升为战略性、目标导向执行者的基础能力。现代大语言模型提供了核心支撑,能够自主将高层次目标拆解为连贯且可执行的步骤。该模式既可用于简单的线性任务(如 CrewAI 智能体制定并遵循写作计划),也可扩展到更复杂、更加动态的系统。以 Google 深度研究智能体为例,它能制定迭代性的研究计划,并根据获取的信息持续不断调整和演进。总体而言,规划模式在人类意图转化为自动化执行方面起到桥梁作用,使智能体能够管理复杂流程并产出全面、综合的结果。
References | 参考文献
-
Google DeepResearch (Gemini Feature): gemini.google.com
Google 深度研究(Gemini 功能):gemini.google.com
-
OpenAI, Introducing deep research: https://openai.com/index/introducing-deep-research/
OpenAI 深度研究介绍:https://openai.com/index/introducing-deep-research/
-
Perplexity, Introducing Perplexity Deep Research: https://www.perplexity.ai/hub/blog/introducing-perplexity-deep-research
Perplexity 深度研究介绍:https://www.perplexity.ai/hub/blog/introducing-perplexity-deep-research