Chapter 14: Knowledge Retrieval RAG
Chapter 14: Knowledge Retrieval (RAG) | 第 14 章:知识检索(RAG)
LLMs exhibit substantial capabilities in generating human-like text. However, their knowledge base is typically confined to the data on which they were trained, limiting their access to real-time information, specific company data, or highly specialized details. Knowledge Retrieval (RAG, or Retrieval Augmented Generation), addresses this limitation. RAG enables LLMs to access and integrate external, current, and context-specific information, thereby enhancing the accuracy, relevance, and factual basis of their outputs.
大语言模型(LLM)在生成类人文本方面表现出强大的能力。然而,它们的知识库通常受限于其训练数据,而这限制了它们获取实时信息、特定的公司数据或高度专业化细节的能力。知识检索(RAG,即检索增强生成)解决了这一限制。RAG 使 LLM 能够访问并整合外部的、当前的、特定上下文的信息,从而增强其输出的准确性、相关性和事实基础。
For AI agents, this is crucial as it allows them to ground their actions and responses in real-time, verifiable data beyond their static training. This capability enables them to perform complex tasks accurately, such as accessing the latest company policies to answer a specific question or checking current inventory before placing an order. By integrating external knowledge, RAG transforms agents from simple conversationalists into effective, data-driven tools capable of executing meaningful work.
对于 AI 智能体而言,这一点至关重要,因为它允许智能体将其行动和响应建立在实时的、可验证的数据之上,而不仅仅是静态的训练数据。这种能力使它们能够准确地执行复杂任务,例如访问最新的公司政策以回答特定问题,或在下单前检查当前库存。通过整合外部知识,RAG 将智能体从简单的对话者转变为高效的数据驱动工具,并能够执行有意义的工作。
Knowledge Retrieval (RAG) Pattern Overview | 知识检索(RAG)模式概述
The Knowledge Retrieval (RAG) pattern significantly enhances the capabilities of LLMs by granting them access to external knowledge bases before generating a response. Instead of relying solely on their internal, pre-trained knowledge, RAG allows LLMs to "look up" information, much like a human might consult a book or search the internet. This process empowers LLMs to provide more accurate, up-to-date, and verifiable answers.
知识检索(RAG)模式通过在生成响应前授予 LLM 访问外部知识库的权限,从而显著增强其能力。RAG 允许 LLM 「查找」信息,而不是仅仅依赖其内部的、预训练的知识,就像人类可能查阅书籍或搜索互联网一样。这一过程使 LLM 能够提供更准确、最新且可验证的答案。
When a user poses a question or gives a prompt to an AI system using RAG, the query isn't sent directly to the LLM. Instead, the system first scours a vast external knowledge base—a highly organized library of documents, databases, or web pages—for relevant information. This search is not a simple keyword match; it's a "semantic search" that understands the user's intent and the meaning behind their words. This initial search pulls out the most pertinent snippets or "chunks" of information. These extracted pieces are then "augmented," or added, to the original prompt, creating a richer, more informed query. Finally, this enhanced prompt is sent to the LLM. With this additional context, the LLM can generate a response that is not only fluent and natural but also factually grounded in the retrieved data.
当用户向带 RAG 的 AI 系统提出问题或发出提示词(Prompt)时,该查询不会直接发送给 LLM。相反,系统首先会搜索一个庞大的外部知识库——一个高度组织的文档、数据或网页库——以获取相关信息。这种搜索不是简单的关键字匹配,而是一种能理解用户意图和言语背后含义的「语义搜索」。初步搜索会提取出最相关的信息片段或「信息块」。这些提取出的片段随后被「增强」或添加到原始 Prompt 中,创建出一个内容更丰富、信息更全面的查询。最后,这个增强后的 Prompt 被发送给 LLM。借助这些检索数据提供的附加上下文,LLM 能够生成一个流畅自然且有事实依据的响应。
The RAG framework provides several significant benefits. It allows LLMs to access up-to-date information, thereby overcoming the constraints of their static training data. This approach also reduces the risk of "hallucination"—the generation of false information—by grounding responses in verifiable data. Moreover, LLMs can utilize specialized knowledge found in internal company documents or wikis. A vital advantage of this process is the capability to offer "citations," which pinpoint the exact source of information, thereby enhancing the trustworthiness and verifiability of the AI's responses.
RAG 框架带来了几项显著优势。它允许 LLM 访问最新信息,从而克服了其静态训练数据的限制。这种方法将响应建立在可验证数据的基础之上,降低了「幻觉」(即生成虚假信息)的风险。此外,LLM 还可以利用公司内部文档或 wiki 中的专业知识。该过程的关键优势是能够提供「引用」,指明信息的具体来源,从而增强 AI 响应的可信度和可验证性。
To fully appreciate how RAG functions, it's essential to understand a few core concepts (see Fig.1):
为了全面理解 RAG 的工作原理,必须掌握几个核心概念(见图 1):
Embeddings: In the context of LLMs, embeddings are numerical representations of text, such as words, phrases, or entire documents. These representations are in the form of a vector, which is a list of numbers. The key idea is to capture the semantic meaning and the relationships between different pieces of text in a mathematical space. Words or phrases with similar meanings will have embeddings that are closer to each other in this vector space. For instance, imagine a simple 2D graph. The word "cat" might be represented by the coordinates (2, 3), while "kitten" would be very close at (2.1, 3.1). In contrast, the word "car" would have a distant coordinate like (8, 1), reflecting its different meaning. In reality, these embeddings are in a much higher-dimensional space with hundreds or even thousands of dimensions, allowing for a very nuanced understanding of language.
嵌入(Embeddings):在 LLM 的语境中,嵌入是以数字形式表示文本,例如词语、短语或整个文档。这些表示以向量(即数字的列表)的形式存在。其核心思想是在一个数学空间中捕捉不同文本片段之间的语义含义和关系。含义相近的词语或短语,其嵌入在向量空间中的距离也更近。例如,在一个简单的二维图表中,「cat」(猫)一词可能由坐标 (2, 3) 表示,而「kitten」(小猫)也会位于非常接近的 (2.1, 3.1)。相比之下,「car」(小汽车)一词的坐标则可能在很远的位置,如 (8, 1),反映了其不同的含义。实际上,这些嵌入存在于维度高得多的空间中,拥有数百甚至数千个维度,从而能够对语言有非常细致的理解。
Text Similarity: Text similarity refers to the measure of how alike two pieces of text are. This can be at a surface level, looking at the overlap of words (lexical similarity), or at a deeper, meaning-based level. In the context of RAG, text similarity is crucial for finding the most relevant information in the knowledge base that corresponds to a user's query.
文本相似度:文本相似度是衡量两段文本相似程度的指标。既可以是表层的词语重叠度(词汇的相似度),也可以是更深层次的、基于含义的相似度。RAG 语境下的文本相似度对于在知识库中找到与用户查询最相关的信息至关重要。
For instance, consider the sentences: "What is the capital of France?" and "Which city is the capital of France?". While the wording is different, they are asking the same question. A good text similarity model would recognize this and assign a high similarity score to these two sentences, even though they only share a few words. This is often calculated using the embeddings of the texts.
例如,「What is the capital of France?」(法国的首都是哪里?)和「Which city is the capital of France?」(哪个城市是法国的首都?)这两个句子,虽然措辞不同,但问的是同一个问题。一个好的文本相似度模型会识别到这一点,并给予这两个句子很高的相似度得分,即使它们只有少数几个相同的词。通常这就是通过计算文本的嵌入来实现的。
Semantic Similarity and Distance: Semantic similarity is a more advanced form of text similarity that focuses purely on the meaning and context of the text, rather than just the words used. It aims to understand if two pieces of text convey the same concept or idea. Semantic distance is the inverse of this; a high semantic similarity implies a low semantic distance, and vice versa. In RAG, semantic search relies on finding documents with the smallest semantic distance to the user's query.
语义相似度与距离:语义相似度是一种更高级的文本相似度形式,它纯粹关注文本的含义和上下文,而不仅仅是所用的词语。其目标是理解两段文本是否传达了相同的概念或思想。语义距离与语义相似度相反;高语义相似度意味着低语义距离,反之亦然。在 RAG 中,语义搜索依赖于找到与用户查询语义距离最小的文档。
For instance, the phrases "a furry feline companion" and "a domestic cat" have no words in common besides "a". However, a model that understands semantic similarity would recognize that they refer to the same thing and would consider them to be highly similar. This is because their embeddings would be very close in the vector space, indicating a small semantic distance. This is the "smart search" that allows RAG to find relevant information even when the user's wording doesn't exactly match the text in the knowledge base.
例如,「a furry feline companion」和「a domestic cat」除了「a」之外没有共同的词语。然而,一个理解语义相似度的模型会识别出它们指的是同一事物,并认为它们高度相似。这是因为它们的嵌入在向量空间中会非常接近,表明语义距离很小,这正是「智能搜索」的体现。有了它,即使在用户的措辞与知识库中的文本不完全匹配时,RAG 也能找到相关信息。
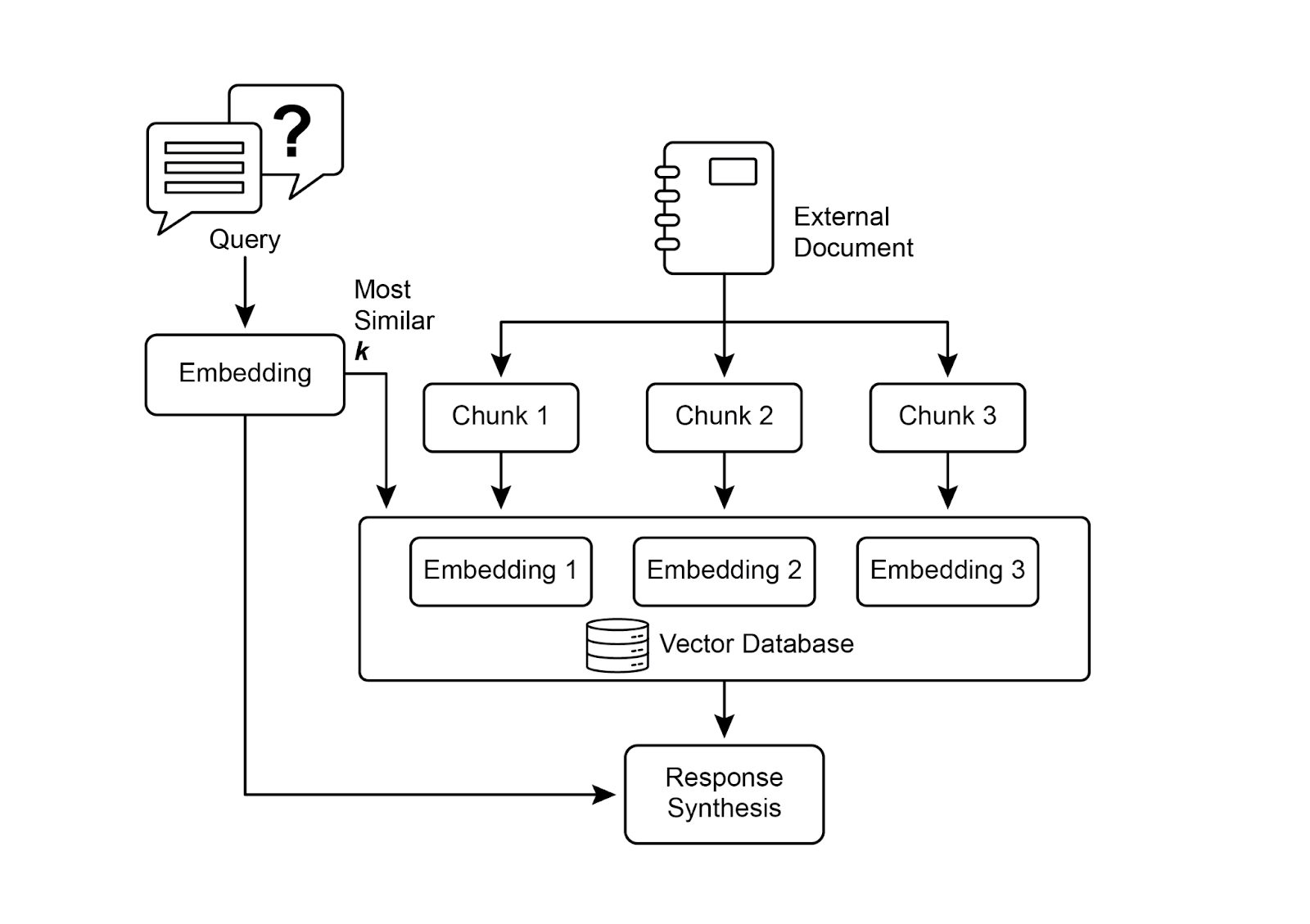
Fig.1: RAG Core Concepts: Chunking, Embeddings, and Vector Database 图 1:RAG 核心概念:分块、嵌入和向量数据库
Chunking of Documents: Chunking is the process of breaking down large documents into smaller, more manageable pieces, or "chunks." For a RAG system to work efficiently, it cannot feed entire large documents into the LLM. Instead, it processes these smaller chunks. The way documents are chunked is important for preserving the context and meaning of the information.
文档分块:分块是将大型文档分解成更小、更易于管理的小块或「块」(chunks)的过程。为了让 RAG 系统高效工作,不能将整个大型文档输入给 LLM,而是处理这些较小的块。文档的分块方式对于保留信息的上下文和含义非常重要。
For instance, instead of treating a 50-page user manual as a single block of text, a chunking strategy might break it down into sections, paragraphs, or even sentences. For instance, a section on "Troubleshooting" would be a separate chunk from the "Installation Guide." When a user asks a question about a specific problem, the RAG system can then retrieve the most relevant troubleshooting chunk, rather than the entire manual. This makes the retrieval process faster and the information provided to the LLM more focused and relevant to the user's immediate need.
例如,一份 50 页的用户手册不会被其视为一整块文本,分块策略会将其分解为章节、段落甚至句子。比如,「故障排除」章节将与「安装指南」分为不同的块。当用户询问特定问题时,RAG 系统就会检索到与故障排除最相关的块,而不是整本手册。这使得检索过程更快,提供给 LLM 的信息也更聚集、更贴合用户的即时需求。
Once documents are chunked, the RAG system must employ a retrieval technique to find the most relevant pieces for a given query. The primary method is vector search, which uses embeddings and semantic distance to find chunks that are conceptually similar to the user's question. An older, but still valuable, technique is BM25, a keyword-based algorithm that ranks chunks based on term frequency without understanding semantic meaning. To get the best of both worlds, hybrid search approaches are often used, combining the keyword precision of BM25 with the contextual understanding of semantic search. This fusion allows for more robust and accurate retrieval, capturing both literal matches and conceptual relevance.
文档分块后,RAG 系统必须采用检索技术来为特定的查询找到最相关的片段。主要方法是向量搜索,它利用嵌入和语义距离来寻找与用户问题具有相似概念的块。BM25 是另一种较早但仍有价值的技术,它是一种基于关键字的算法,不能理解语义,仅根据词频对块进行排序。为了兼得两者之长,通常会采用混合搜索方法,将 BM25 的关键字精度与语义搜索的上下文理解相结合。这种融合实现了更稳健与准确的检索,既能捕捉字面的匹配,又能把握概念的相关性。
Vector databases: A vector database is a specialized type of database designed to store and query embeddings efficiently. After documents are chunked and converted into embeddings, these high-dimensional vectors are stored in a vector database. Traditional retrieval techniques, like keyword-based search, are excellent at finding documents containing exact words from a query but lack a deep understanding of language. They wouldn't recognize that "furry feline companion" means "cat." This is where vector databases excel. They are built specifically for semantic search. By storing text as numerical vectors, they can find results based on conceptual meaning, not just keyword overlap.
向量数据库:向量数据库是一种专门用于高效存储和查询嵌入的专用类型数据库。在文档被分块并转换为嵌入后,这些高维向量被存储在向量数据库中。传统的检索技术,如基于关键字的搜索,善于查找到包含查询中出现确切词语的文档,但缺乏对语言的深入理解。它们无法识别出「毛茸茸的猫科动物伴侣」就是「猫」的意思,而这正是向量数据库的优势所在。它们专为语义搜索而构建。通过将文本存储为数字向量,它们可以根据概念含义来查找结果,而非仅仅依赖关键字重叠。
When a user's query is also converted into a vector, the database uses highly optimized algorithms (like HNSW - Hierarchical Navigable Small World) to rapidly search through millions of vectors and find the ones that are "closest" in meaning. This approach is far superior for RAG because it uncovers relevant context even if the user's phrasing is completely different from the source documents. In essence, while other techniques search for words, vector databases search for meaning.
当用户的查询也被转换为向量时,数据库会使用高度优化的算法(如 HNSW - Hierarchical Navigable Small World)快速在数百万个向量中搜索,并找到在含义上「最接近」的向量。这种方法对 RAG 来说要优越得多,因为即使在用户的措辞与源文档完全不同的情况下,它也能发现相关上下文。本质上,其他技术搜索的是词语,而向量数据库搜索的是含义。
This technology is implemented in various forms, from managed databases like Pinecone and Weaviate to open-source solutions such as Chroma DB, Milvus, and Qdrant. Even existing databases can be augmented with vector search capabilities, as seen with Redis, Elasticsearch, and Postgres (using the pgvector extension). The core retrieval mechanisms are often powered by libraries like Meta AI's FAISS or Google Research's ScaNN, which are fundamental to the efficiency of these systems.
这项技术有多种实现形式,从像 Pinecone 和 Weaviate 这样的托管数据库,到 Chroma DB、Milvus 和 Qdrant 等开源解决方案。即使是现有数据库,例如 Redis、Elasticsearch 和 Postgres(使用 pgvector 扩展),也可以使用向量搜索功能进行增强。核心检索机制通常由 Meta AI 的 FAISS 或 Google Research 的 ScaNN 等库提供支持,这些库对系统的效率至关重要。
RAG's Challenges: Despite its power, the RAG pattern is not without its challenges. A primary issue arises when the information needed to answer a query is not confined to a single chunk but is spread across multiple parts of a document or even several documents. In such cases, the retriever might fail to gather all the necessary context, leading to an incomplete or inaccurate answer.
RAG 的挑战:尽管功能强大,RAG 模式也并非没有挑战。一个主要问题是,当回答一个查询所需的信息无法在单个块满足,而是分散在文档的多个部分甚至多个文档中时,检索器可能无法收集到所有需要的上下文,导致答案不完整或不准确。
The system's effectiveness is also highly dependent on the quality of the chunking and retrieval process; if irrelevant chunks are retrieved, it can introduce noise and confuse the LLM. Furthermore, effectively synthesizing information from potentially contradictory sources remains a significant hurdle for these systems.
系统的有效性也高度依赖于分块和检索过程的质量;如果检索到不相关的块,会引入噪声并迷惑 LLM。此外,系统面临的一个重大阻碍是有效地综合可能相互矛盾的来源信息。
Besides that, another challenge is that RAG requires the entire knowledge base to be pre-processed and stored in specialized databases, such as vector or graph databases, which is a considerable undertaking. Consequently, this knowledge requires periodic reconciliation to remain up-to-date, a crucial task when dealing with evolving sources like company wikis. This entire process can have a noticeable impact on performance, increasing latency, operational costs, and the number of tokens used in the final prompt.
除此之外,另一个挑战是 RAG 要求整个知识库都经过预处理,并且存储在专门的数据库中,如向量数据库或图数据库。这是一项相当大的工程。因此,这些知识需要定期的同步以保持更新。在处理像公司维基这样不断变化的来源时,这就是一项至关重要的任务。整个过程可能对性能产生显著影响,增加延迟、运营成本以及最终 Prompt 中使用的 token 数量。
In summary, the Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) pattern represents a significant leap forward in making AI more knowledgeable and reliable. By seamlessly integrating an external knowledge retrieval step into the generation process, RAG addresses some of the core limitations of standalone LLMs. The foundational concepts of embeddings and semantic similarity, combined with retrieval techniques like keyword and hybrid search, allow the system to intelligently find relevant information, which is made manageable through strategic chunking.
总之,检索增强生成(RAG)模式在使 AI 的知识更渊博、更可靠方面,产生了巨大飞跃。通过将外部知识检索无缝集成到生成过程中,RAG 解决了单用 LLM 时的一些核心局限。嵌入和语义相似度等基础概念,结合关键字和混合搜索等检索技术,使系统能够智能地找到相关信息,并通过策略性分块使其变得易于管理。
This entire retrieval process is powered by specialized vector databases designed to store and efficiently query millions of embeddings at scale. While challenges in retrieving fragmented or contradictory information persist, RAG empowers LLMs to produce answers that are not only contextually appropriate but also anchored in verifiable facts, fostering greater trust and utility in AI.
整个检索过程由专门的向量数据库提供支持,这些数据库旨在存储并高效的处理针对数百万个嵌入的大规模查询。尽管在检索碎片化或矛盾信息方面仍然存在挑战,但 RAG 使 LLM 能够生成符合上下文的,且基于可验证事实的答案,从而增强了人们对 AI 的信任和应用价值。
Graph RAG: GraphRAG is an advanced form of Retrieval-Augmented Generation that utilizes a knowledge graph instead of a simple vector database for information retrieval. It answers complex queries by navigating the explicit relationships (edges) between data entities (nodes) within this structured knowledge base. A key advantage is its ability to synthesize answers from information fragmented across multiple documents, a common failing of traditional RAG. By understanding these connections, GraphRAG provides more contextually accurate and nuanced responses.
图 RAG(Graph RAG):GraphRAG 是一种先进的 RAG 形式,它利用知识图谱而非简单的向量数据库进行信息检索。它通过在结构化知识库中导航数据实体(节点)之间的显式关系(边)来回答复杂查询。其一个关键优势是能够综合来自多个文档中的碎片化信息来生成答案,而这正是传统 RAG 的一个常见短板。通过理解这些联系,GraphRAG 能够提供与上下文相符、更细致的响应。
Use cases include complex financial analysis, connecting companies to market events, and scientific research for discovering relationships between genes and diseases. The primary drawback, however, is the significant complexity, cost, and expertise required to build and maintain a high-quality knowledge graph. This setup is also less flexible and can introduce higher latency compared to simpler vector search systems. The system's effectiveness is entirely dependent on the quality and completeness of the underlying graph structure. Consequently, GraphRAG offers superior contextual reasoning for intricate questions but at a much higher implementation and maintenance cost. In summary, it excels where deep, interconnected insights are more critical than the speed and simplicity of standard RAG.
其用例包括复杂的金融分析、将公司与市场事件联系起来,以及用于发现基因和疾病之间关系的科学研究。然而,其主要缺点是构建和维护高质量知识图谱带来的巨大复杂性、成本和专业知识。与更简单的向量搜索系统相比,这个系统的灵活性也较差,并且可能引入更高的延迟。系统的有效性完全取决于底层图结构的质量和完整性。因此,GraphRAG 为复杂问题提供了卓越的上下文推理能力,但实现和维护成本要高得多。总而言之,GraphRAG 在需要进行深度互联洞察的场景上,相较于标准 RAG 的速度和简单性,其表现更处出色。
Agentic RAG: An evolution of this pattern, known as Agentic RAG (see Fig.2), introduces a reasoning and decision-making layer to significantly enhance the reliability of information extraction. Instead of just retrieving and augmenting, an "agent"—a specialized AI component—acts as a critical gatekeeper and refiner of knowledge. Rather than passively accepting the initially retrieved data, this agent actively interrogates its quality, relevance, and completeness, as illustrated by the following scenarios.
智能体式 RAG(Agentic RAG):该模式的一个演进版本,被称为智能体式 RAG(见图 2),引入了一个推理和决策层,以显著提高信息提取的可靠性。一个「智能体」——一个专门的 AI 组件——不仅是检索和增强信息,还扮演着知识守门员和提炼者的关键角色。它不是被动地接受初步检索到的数据,而是主动审查其质量、相关性和完整性,如下列场景所示。
First, an agent excels at reflection and source validation. If a user asks, "What is our company's policy on remote work?" a standard RAG might pull up a 2020 blog post alongside the official 2025 policy document. The agent, however, would analyze the documents' metadata, recognize the 2025 policy as the most current and authoritative source, and discard the outdated blog post before sending the correct context to the LLM for a precise answer.
首先,智能体擅长反思和来源验证。如果用户问:「我们公司关于远程工作的政策是什么?」标准的 RAG 可能会同时找出一篇 2020 年的博客文章和 2025 年的官方政策文件。智能体则会分析这些文件的元数据,识别出 2025 年的政策是最新、最权威的来源,并舍弃掉过时的博客文章,只将正确的上下文发送给 LLM 以获得精确答案。
 Fig.2: Agentic RAG introduces a reasoning agent that actively evaluates, reconciles, and refines retrieved information to ensure a more accurate and trustworthy final response.
Fig.2: Agentic RAG introduces a reasoning agent that actively evaluates, reconciles, and refines retrieved information to ensure a more accurate and trustworthy final response.
图 2:智能体式 RAG 引入了一个推理智能体,主动评估、协调和提炼检索到的信息,以确保最终响应更准确、更可信。
Second, an agent is adept at reconciling knowledge conflicts. Imagine a financial analyst asks, "What was Project Alpha's Q1 budget?" The system retrieves two documents: an initial proposal stating a €50,000 budget and a finalized financial report listing it as €65,000. An Agentic RAG would identify this contradiction, prioritize the financial report as the more reliable source, and provide the LLM with the verified figure, ensuring the final answer is based on the most accurate data.
其次,智能体善于解决知识冲突。想象一位财务分析师问:「Alpha 项目第一季度的预算是多少?」系统检索到两份文件:一份是初步提案,预算为 50,000 欧元;另一份是最终财务报告,预算为 65,000 欧元。一个智能体式 RAG 会识别出这种矛盾,将财务报告作为更可靠的来源优先处理,并向 LLM 提供核实后的数字,确保最终答案基于最准确的数据。
Third, an agent can perform multi-step reasoning to synthesize complex answers. If a user asks, "How do our product's features and pricing compare to Competitor X's?" the agent would decompose this into separate sub-queries. It would initiate distinct searches for its own product's features, its pricing, Competitor X's features, and Competitor X's pricing. After gathering these individual pieces of information, the agent would synthesize them into a structured, comparative context before feeding it to the LLM, enabling a comprehensive response that a simple retrieval could not have produced.
第三,智能体可以执行多步推理来综合复杂答案。如果用户问:「我们的产品特性和定价与竞争对手 X 相比如何?」智能体会将此问题分解为独立的子查询。它会分别搜索自己产品的特性、定价,以及竞争对手 X 的特性、定价。在收集完这些独立信息后,智能体会将它们综合成一个结构化的、可比较的上下文,然后再提供给 LLM,从而生成一个简单检索无法产生的全面答案。
Fourth, an agent can identify knowledge gaps and use external tools. Suppose a user asks, "What was the market's immediate reaction to our new product launched yesterday?" The agent searches the internal knowledge base, which is updated weekly, and finds no relevant information. Recognizing this gap, it can then activate a tool—such as a live web-search API—to find recent news articles and social media sentiment. The agent then uses this freshly gathered external information to provide an up-to-the-minute answer, overcoming the limitations of its static internal database.
第四,智能体可以识别知识差距并使用外部工具。假设一个用户问:「市场对我们昨天发布的新产品有何即时反应?」智能体在每周更新的内部知识库中搜索,没有发现相关信息。识别到这一差距后,它可以激活一个工具——例如一个实时网络搜索 API——来查找最近的新闻文章和社交媒体情绪。然后,智能体利用这些新收集的外部信息提供一个最新的答案,克服了公司内部静态数据库的局限性。
Challenges of Agentic RAG: While powerful, the agentic layer introduces its own set of challenges. The primary drawback is a significant increase in complexity and cost. Designing, implementing, and maintaining the agent's decision-making logic and tool integrations requires substantial engineering effort and adds to computational expenses. This complexity can also lead to increased latency, as the agent's cycles of reflection, tool use, and multi-step reasoning take more time than a standard, direct retrieval process. Furthermore, the agent itself can become a new source of error; a flawed reasoning process could cause it to get stuck in useless loops, misinterpret a task, or improperly discard relevant information, ultimately degrading the quality of the final response.
智能体式 RAG 的挑战:虽然功能强大,但智能体层也带来了其自身的挑战。主要缺点是复杂性和成本显著增加。设计、实现和维护智能体的决策逻辑及工具集成需要大量的工程投入,并增加了计算开销。这种复杂性也导致延迟增加,因为智能体的反思、工具使用和多步推理周期比标准的直接检索流程要花费更多时间。此外,智能体本身也可能成为新的错误来源;一个有缺陷的推理过程可能导致它陷入无用的循环、错误理解任务或不当的丢弃相关信息,降低最终的响应质量。
In summary: Agentic RAG represents a sophisticated evolution of the standard retrieval pattern, transforming it from a passive data pipeline into an active, problem-solving framework. By embedding a reasoning layer that can evaluate sources, reconcile conflicts, decompose complex questions, and use external tools, agents dramatically improve the reliability and depth of the generated answers. This advancement makes the AI more trustworthy and capable, though it comes with important trade-offs in system complexity, latency, and cost that must be carefully managed.
总结:智能体式 RAG 代表了标准检索模式的精巧演进,将其从一个被动的数据管道转变为一个主动的问题解决框架。通过嵌入一个能够评估来源、协调冲突、分解复杂问题并使用外部工具的推理层,智能体极大地提高了生成答案的可靠性和深度。这一进步使 AI 更加值得信赖和能干,尽管它需要仔细管理系统复杂性、延迟和成本方面的重要权衡。
Practical Applications & Use Cases | 实践应用与用例
Knowledge Retrieval (RAG) is changing how Large Language Models (LLMs) are utilized across various industries, enhancing their ability to provide more accurate and contextually relevant responses.
知识检索(RAG)正在改变大语言模型(LLM)在各行各业的应用方式,使它们能够提供更准确、更具上下文相关性响应的能力。
Applications include:
应用包括:
-
Enterprise Search and Q&A: Organizations can develop internal chatbots that respond to employee inquiries using internal documentation such as HR policies, technical manuals, and product specifications. The RAG system extracts relevant sections from these documents to inform the LLM's response.
-
企业搜索与问答:组织可以开发内部聊天机器人,利用人力资源政策、技术手册和产品规格等内部文档来回应员工的询问。RAG 系统从这些文档中提取相关部分,为 LLM 的响应提供信息。
-
Customer Support and Helpdesks: RAG-based systems can offer precise and consistent responses to customer queries by accessing information from product manuals, frequently asked questions (FAQs), and support tickets. This can reduce the need for direct human intervention for routine issues.
-
客户支持与服务台:基于 RAG 的系统可以通过访问产品手册、常见问题解答(FAQ)和支持工单中的信息,为客户查询提供精确且一致的响应。这可以减少常规问题上人工干预的需求。
-
Personalized Content Recommendation: Instead of basic keyword matching, RAG can identify and retrieve content (articles, products) that is semantically related to a user's preferences or previous interactions, leading to more relevant recommendations.
-
个性化内容推荐:RAG 不再是简单的关键字匹配,而是能够识别并检索与用户偏好或历史互动的语义相关内容(文章、产品),提供更具相关性的推荐。
-
News and Current Events Summarization: LLMs can be integrated with real-time news feeds. When prompted about a current event, the RAG system retrieves recent articles, allowing the LLM to produce an up-to-date summary.
-
新闻与时事摘要:LLM 可以与实时新闻源集成。当被问及某个时事时,RAG 系统会检索最近的文章,使 LLM 能够生成最新的摘要。
By incorporating external knowledge, RAG extends the capabilities of LLMs beyond simple communication to function as knowledge processing systems.
通过整合外部知识,RAG 将 LLM 的能力从简单的通信扩展到作为知识处理系统来工作。
Hands-On Code Example (ADK) | 使用 ADK 的实战代码
To illustrate the Knowledge Retrieval (RAG) pattern, let's see three examples.
为了说明知识检索(RAG)模式,我们来看三个例子。
First, is how to use Google Search to do RAG and ground LLMs to search results. Since RAG involves accessing external information, the Google Search tool is a direct example of a built-in retrieval mechanism that can augment an LLM's knowledge.
首先,是如何使用 Google Search 进行 RAG,并基于搜索结果让 LLM 回答。由于 RAG 涉及访问外部信息,Google Search 工具是一个具备内置检索机制,能够增强 LLM 知识的的直接例子。
from google.adk.tools import google_search
from google.adk.agents import Agent
search_agent = Agent(
name="research_assistant",
model="gemini-2.0-flash-exp",
instruction="You help users research topics. When asked, use the Google Search tool",
tools=[google_search]
)
Second, this section explains how to utilize Vertex AI RAG capabilities within the Google ADK. The code provided demonstrates the initialization of VertexAiRagMemoryService from the ADK. This allows for establishing a connection to a Google Cloud Vertex AI RAG Corpus. The service is configured by specifying the corpus resource name and optional parameters such as SIMILARITY_TOP_K and VECTOR_DISTANCE_THRESHOLD. These parameters influence the retrieval process. SIMILARITY_TOP_K defines the number of top similar results to be retrieved. VECTOR_DISTANCE_THRESHOLD sets a limit on the semantic distance for the retrieved results. This setup enables agents to perform scalable and persistent semantic knowledge retrieval from the designated RAG Corpus. The process effectively integrates Google Cloud's RAG functionalities into an ADK agent, thereby supporting the development of responses grounded in factual data.
其次,本节说明了如何在 Google ADK 中利用 Vertex AI RAG 功能。提供的代码演示了如何从 ADK 初始化 VertexAiRagMemoryService。这允许建立到 Google Cloud Vertex AI RAG 语料库的连接。通过指定语料库资源名称以及可选参数(如 SIMILARITY_TOP_K 和 VECTOR_DISTANCE_THRESHOLD)来配置该服务。这些参数会影响检索过程。SIMILARITY_TOP_K 定义了要检索的最相似结果数量。VECTOR_DISTANCE_THRESHOLD 为检索结果的语义距离设置了一个限制。此设置使智能体能够从指定的 RAG 语料库中执行可扩展且持久的语义知识检索。该过程有效地将 Google Cloud 的 RAG 功能集成到 ADK 智能体中,从而支持开发基于事实数据的响应。
# Import the necessary VertexAiRagMemoryService class from the google.adk.memory module.
from google.adk.memory import VertexAiRagMemoryService
RAG_CORPUS_RESOURCE_NAME = "projects/your-gcp-project-id/locations/us-central1/ragCorpora/your-corpus-id"
# Define an optional parameter for the number of top similar results to retrieve.
# This controls how many relevant document chunks the RAG service will return.
SIMILARITY_TOP_K = 5
# Define an optional parameter for the vector distance threshold.
# This threshold determines the maximum semantic distance allowed for retrieved results;
# results with a distance greater than this value might be filtered out.
VECTOR_DISTANCE_THRESHOLD = 0.7
# Initialize an instance of VertexAiRagMemoryService.
# This sets up the connection to your Vertex AI RAG Corpus.
# - rag_corpus: Specifies the unique identifier for your RAG Corpus.
# - similarity_top_k: Sets the maximum number of similar results to fetch.
# - vector_distance_threshold: Defines the similarity threshold for filtering results.
memory_service = VertexAiRagMemoryService(
rag_corpus=RAG_CORPUS_RESOURCE_NAME,
similarity_top_k=SIMILARITY_TOP_K,
vector_distance_threshold=VECTOR_DISTANCE_THRESHOLD
)
Hands-On Code Example (LangChain) | 使用 LangChain 的实战代码
Third, let's walk through a complete example using LangChain.
第三,让我们用 LangChain 来看一个完整的例子。
import os
import requests
from typing import List, Dict, Any, TypedDict
from langchain_community.document_loaders import TextLoader
from langchain_core.documents import Document
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
from langchain_community.embeddings import OpenAIEmbeddings
from langchain_community.vectorstores import Weaviate
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.text_splitter import CharacterTextSplitter
from langchain.schema.runnable import RunnablePassthrough
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, END
import weaviate
from weaviate.embedded import EmbeddedOptions
import dotenv
# Load environment variables (e.g., OPENAI_API_KEY)
dotenv.load_dotenv()
# Set your OpenAI API key (ensure it's loaded from .env or set here)
# os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY"
# --- 1. Data Preparation (Preprocessing) ---
# Load data
url = "https://github.com/langchain-ai/langchain/blob/master/docs/docs/how_to/state_of_the_union.txt"
res = requests.get(url)
with open("state_of_the_union.txt", "w") as f:
f.write(res.text)
loader = TextLoader('./state_of_the_union.txt')
documents = loader.load()
# Chunk documents
text_splitter = CharacterTextSplitter(chunk_size=500, chunk_overlap=50)
chunks = text_splitter.split_documents(documents)
# Embed and store chunks in Weaviate
client = weaviate.Client(
embedded_options = EmbeddedOptions()
)
vectorstore = Weaviate.from_documents(
client = client,
documents = chunks,
embedding = OpenAIEmbeddings(),
by_text = False
)
# Define the retriever
retriever = vectorstore.as_retriever()
# Initialize LLM
llm = ChatOpenAI(model_name="gpt-3.5-turbo", temperature=0)
# --- 2. Define the State for LangGraph ---
class RAGGraphState(TypedDict):
question: str
documents: List[Document]
generation: str
# --- 3. Define the Nodes (Functions) ---
def retrieve_documents_node(state: RAGGraphState) -> RAGGraphState:
"""Retrieves documents based on the user's question."""
question = state["question"]
documents = retriever.invoke(question)
return {"documents": documents, "question": question, "generation": ""}
def generate_response_node(state: RAGGraphState) -> RAGGraphState:
"""Generates a response using the LLM based on retrieved documents."""
question = state["question"]
documents = state["documents"]
# Prompt template from the PDF
template = """You are an assistant for question-answering tasks.
Use the following pieces of retrieved context to answer the question.
If you don't know the answer, just say that you don't know.
Use three sentences maximum and keep the answer concise.
Question: {question}
Context: {context}
Answer:"""
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(template)
# Format the context from the documents
context = "\n\n".join([doc.page_content for doc in documents])
# Create the RAG chain
rag_chain = prompt | llm | StrOutputParser()
# Invoke the chain
generation = rag_chain.invoke({"context": context, "question": question})
return {"question": question, "documents": documents, "generation": generation}
# --- 4. Build the LangGraph Graph ---
workflow = StateGraph(RAGGraphState)
# Add nodes
workflow.add_node("retrieve", retrieve_documents_node)
workflow.add_node("generate", generate_response_node)
# Set the entry point
workflow.set_entry_point("retrieve")
# Add edges (transitions)
workflow.add_edge("retrieve", "generate")
workflow.add_edge("generate", END)
# Compile the graph
app = workflow.compile()
# --- 5. Run the RAG Application ---
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("\n--- Running RAG Query ---")
query = "What did the president say about Justice Breyer"
inputs = {"question": query}
for s in app.stream(inputs):
print(s)
print("\n--- Running another RAG Query ---")
query_2 = "What did the president say about the economy?"
inputs_2 = {"question": query_2}
for s in app.stream(inputs_2):
print(s)
This Python code illustrates a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) pipeline implemented with LangChain and LangGraph. The process begins with the creation of a knowledge base derived from a text document, which is segmented into chunks and transformed into embeddings. These embeddings are then stored in a Weaviate vector store, facilitating efficient information retrieval.
这段 Python 代码展示了用 LangChain 和 LangGraph 实现的检索增强生成(RAG)流水线。该过程首先从一个文本文档创建知识库,该文档被分割成块并转换为嵌入。然后,这些嵌入被存储在 Weaviate 向量存储中,以便进行高效的信息检索。
A StateGraph in LangGraph is utilized to manage the workflow between two key functions: retrieve_documents_node and generate_response_node. The retrieve_documents_node function queries the vector store to identify relevant document chunks based on the user's input. Subsequently, the generate_response_node function utilizes the retrieved information and a predefined prompt template to produce a response using an OpenAI Large Language Model (LLM). The app.stream method allows the execution of queries through the RAG pipeline, demonstrating the system's capacity to generate contextually relevant outputs.
LangGraph 中的 StateGraph 用于管理两个关键函数之间的工作流:retrieve_documents_node 和 generate_response_node。retrieve_documents_node 函数查询向量存储,以根据用户输入识别相关的文档块。随后,generate_response_node 函数利用检索到的信息和预定义的提示词模板,使用 OpenAI 大语言模型(LLM)生成响应。app.stream 方法允许通过 RAG 流水线执行查询,展示了系统生成上下文相关输出的能力。
At a Glance | 要点速览
What: LLMs possess impressive text generation abilities but are fundamentally limited by their training data. This knowledge is static, meaning it doesn't include real-time information or private, domain-specific data. Consequently, their responses can be outdated, inaccurate, or lack the specific context required for specialized tasks. This gap restricts their reliability for applications demanding current and factual answers.
问题所在:大语言模型(LLM)拥有令人印象深刻的文本生成能力,但从根本上受其训练数据的限制。这些知识是静态的,意味着它不包含实时信息或私有的、特定领域的数据。因此,它们的响应可能过时、不准确,或缺乏任务所需的特定上下文。在要求答案及时且基于事实的应用中,这一差距限制了它们的可靠性。
Why: The Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) pattern provides a standardized solution by connecting LLMs to external knowledge sources. When a query is received, the system first retrieves relevant information snippets from a specified knowledge base. These snippets are then appended to the original prompt, enriching it with timely and specific context. This augmented prompt is then sent to the LLM, enabling it to generate a response that is accurate, verifiable, and grounded in external data. This process effectively transforms the LLM from a closed-book reasoner into an open-book one, significantly enhancing its utility and trustworthiness.
解决之道:检索增强生成(RAG)模式通过将 LLM 连接到外部知识源,提供了一个标准化的解决方案。当收到查询时,系统首先从指定的知识库中检索相关信息片段。然后,这些包含及时和特定上下文的片段附加到原始提示词中以丰富它。这个增强后的提示词随后被发送给 LLM,使其能够生成一个准确、可验证且基于外部数据的响应。这个过程有效地将 LLM 从一个「闭卷」推理者转变为一个「开卷」推理者,从而显著增强了其实用性和可信度。
Rule of thumb: Use this pattern when you need an LLM to answer questions or generate content based on specific, up-to-date, or proprietary information that was not part of its original training data. It is ideal for building Q&A systems over internal documents, customer support bots, and applications requiring verifiable, fact-based responses with citations.
经验法则:当你需要 LLM 基于其原始训练数据之外的特定、最新或专有信息,来回答问题或生成内容时,应当使用 RAG 模式。它非常适合用于构建基于内部文档的问答系统、客户支持机器人,以及需要可验证的、基于事实且响应中带引用的的应用。
Visual Summary | 可视化总结
 Knowledge Retrieval pattern: an AI agent to query and retrieve information from structured databases
知识检索模式:一个 AI 智能体查询和检索来自结构化数据库的信息。
Knowledge Retrieval pattern: an AI agent to query and retrieve information from structured databases
知识检索模式:一个 AI 智能体查询和检索来自结构化数据库的信息。
 Fig. 3: Knowledge Retrieval pattern: an AI agent to find and synthesize information from the public internet in response to user queries.
Fig. 3: Knowledge Retrieval pattern: an AI agent to find and synthesize information from the public internet in response to user queries.
图 3:知识检索模式:一个 AI 智能体根据用户查询从公共互联网上查找和综合信息。
Key Takeaways | 核心要点
-
Knowledge Retrieval (RAG) enhances LLMs by allowing them to access external, up-to-date, and specific information.
-
知识检索(RAG)通过允许 LLM 访问外部的、最新的和特定的信息来增强其能力。
-
The process involves Retrieval (searching a knowledge base for relevant snippets) and Augmentation (adding these snippets to the LLM's prompt).
-
该过程包括检索(在知识库中搜索相关片段)和增强(将这些片段添加到 LLM 的提示词中)。
-
RAG helps LLMs overcome limitations like outdated training data, reduces "hallucinations," and enables domain-specific knowledge integration.
-
RAG 帮助 LLM 克服诸如训练数据过时等限制,减少「幻觉」,并实现特定领域知识的整合。
-
RAG allows for attributable answers, as the LLM's response is grounded in retrieved sources.
-
RAG 允许提供可归因的答案,因为 LLM 的响应是基于检索到的来源的。
-
GraphRAG leverages a knowledge graph to understand the relationships between different pieces of information, allowing it to answer complex questions that require synthesizing data from multiple sources.
-
GraphRAG 利用知识图谱来理解不同信息片段之间的关系,使其能够回答需要综合多个来源数据的复杂问题。
-
Agentic RAG moves beyond simple information retrieval by using an intelligent agent to actively reason about, validate, and refine external knowledge, ensuring a more accurate and reliable answer.
-
智能体式 RAG 超越了简单的信息检索,它使用一个智能体来主动地对外部知识进行推理、验证和提炼,从而确保答案更准确、更可靠。
-
Practical applications span enterprise search, customer support, legal research, and personalized recommendations.
-
实际应用涵盖企业搜索、客户支持、法律研究和个性化推荐。
Conclusion | 结语
In conclusion, Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) addresses the core limitation of a Large Language Model's static knowledge by connecting it to external, up-to-date data sources. The process works by first retrieving relevant information snippets and then augmenting the user's prompt, enabling the LLM to generate more accurate and contextually aware responses. This is made possible by foundational technologies like embeddings, semantic search, and vector databases, which find information based on meaning rather than just keywords. By grounding outputs in verifiable data, RAG significantly reduces factual errors and allows for the use of proprietary information, enhancing trust through citations.
总之,检索增强生成(RAG)通过将大语言模型(LLM)连接到外部的、最新的数据源,解决了其静态知识的核心局限。该过程首先检索相关信息片段,然后增强用户的提示词,使 LLM 能够生成更准确、更具上下文感知能力的响应。这得益于嵌入、语义搜索和向量数据库等基础技术,可以根据含义而非仅仅是关键字来查找信息。通过将输出建立在可验证的数据之上,RAG 显著减少了事实性错误,并允许使用专有信息,通过引用增强了可信度。
An advanced evolution, Agentic RAG, introduces a reasoning layer that actively validates, reconciles, and synthesizes retrieved knowledge for even greater reliability. Similarly, specialized approaches like GraphRAG leverage knowledge graphs to navigate explicit data relationships, allowing the system to synthesize answers to highly complex, interconnected queries.
一个更高级的演进版本,智能体式 RAG,引入了一个推理层,能够主动验证、协调和综合检索到的知识,以获得更高的可靠性。同样,像 GraphRAG 这样的专门方法利用知识图谱来导航显式的数据关系,使系统能够综合回答高度复杂、相互关联的查询。
This agent can resolve conflicting information, perform multi-step queries, and use external tools to find missing data. While these advanced methods add complexity and latency, they drastically improve the depth and trustworthiness of the final response. Practical applications for these patterns are already transforming industries, from enterprise search and customer support to personalized content delivery. Despite the challenges, RAG is a crucial pattern for making AI more knowledgeable, reliable, and useful. Ultimately, it transforms LLMs from closed-book conversationalists into powerful, open-book reasoning tools.
这种智能体可以解决冲突信息,执行多步查询,并使用外部工具查找缺失的数据。虽然这些先进方法增加了复杂性和延迟,但它们极大地提高了最终响应的深度和可信度。这些模式的实际应用已经正在改变各行各业,从企业搜索和客户支持到个性化内容交付。尽管存在挑战,RAG 仍然是使 AI 知识更渊博、更可靠、更有用的关键模式。最终,它将 LLM 从「闭卷」的对话者转变为强大的、「开卷」的推理工具。
References | 参考文献
Lewis, P., et al. (2020). Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Knowledge-Intensive NLP Tasks. https://arxiv.org/abs/2005.11401 Lewis, P., et al. (2020)。知识密集型自然语言处理任务的检索增强生成。https://arxiv.org/abs/2005.11401
Google AI for Developers Documentation. Retrieval Augmented Generation - https://cloud.google.com/vertex-ai/generative-ai/docs/rag-engine/rag-overview Google AI 开发者文档。检索增强生成 - https://cloud.google.com/vertex-ai/generative-ai/docs/rag-engine/rag-overview
Retrieval-Augmented Generation with Graphs (GraphRAG), https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.00309 使用图的检索增强生成 (GraphRAG), https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.00309
LangChain and LangGraph: Leonie Monigatti, "Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG): From Theory to LangChain Implementation," https://medium.com/data-science/retrieval-augmented-generation-rag-from-theory-to-langchain-implementation-4e9bd5f6a4f2 LangChain 与 LangGraph:Leonie Monigatti,「检索增强生成(RAG):从理论到 LangChain 实现」,https://medium.com/data-science/retrieval-augmented-generation-rag-from-theory-to-langchain-implementation-4e9bd5f6a4f2
Google Cloud Vertex AI RAG Corpus https://cloud.google.com/vertex-ai/generative-ai/docs/rag-engine/manage-your-rag-corpus#corpus-management Google Cloud Vertex AI RAG 语料库 https://cloud.google.com/vertex-ai/generative-ai/docs/rag-engine/manage-your-rag-corpus#corpus-management