Chapter 01: Prompt Chaining
Chapter 1: Prompt Chaining | 第一章:提示链
Prompt Chaining Pattern Overview | 提示链模式概述
Prompt chaining, sometimes referred to as Pipeline pattern, represents a powerful paradigm for handling intricate tasks when leveraging large language models (LLMs). Rather than expecting an LLM to solve a complex problem in a single, monolithic step, prompt chaining advocates for a divide-and-conquer strategy. The core idea is to break down the original, daunting problem into a sequence of smaller, more manageable sub-problems. Each sub-problem is addressed individually through a specifically designed prompt, and the output generated from one prompt is strategically fed as input into the subsequent prompt in the chain.
提示链模式,也称为「管道模式」,是利用大语言模型处理复杂任务的一种强大范式。它不期望用单一步骤解决复杂问题,而是采用「分而治之」策略。其核心思想是将难题拆解为一系列更小、更易管理的子问题。每个子问题通过专门设计的提示独立解决,前一步的输出传递给下一步作为输入。
This sequential processing technique inherently introduces modularity and clarity into the interaction with LLMs. By decomposing a complex task, it becomes easier to understand and debug each individual step, making the overall process more robust and interpretable. Each step in the chain can be meticulously crafted and optimized to focus on a specific aspect of the larger problem, leading to more accurate and focused outputs.
这种顺序处理技术天然具备模块化和清晰性特点。通过分解复杂任务,每个独立步骤都变得更易于理解和调试,从而使整个流程更加稳健、更具可解释性。链条中的每一步都可以被精心设计和优化,专注于解决整体问题中的某个特定方面,最终带来更精准、更聚焦的输出。
The output of one step acting as the input for the next is crucial. This passing of information establishes a dependency chain, hence the name, where the context and results of previous operations guide the subsequent processing. This allows the LLM to build on its previous work, refine its understanding, and progressively move closer to the desired solution.
上一步的输出成为下一步的输入,这一点至关重要。这种信息传递建立起一个依赖链(链式结构由此得名),前序操作的上下文和结果引导后续处理。这使得模型能够在先前工作的基础上不断深化理解,逐步接近最终期望的解决方案。
Furthermore, prompt chaining is not just about breaking down problems; it also enables the integration of external knowledge and tools. At each step, the LLM can be instructed to interact with external systems, APIs, or databases, enriching its knowledge and abilities beyond its internal training data. This capability dramatically expands the potential of LLMs, allowing them to function not just as isolated models but as integral components of broader, more intelligent systems.
提示链不仅能分解问题,还能整合外部知识与工具。每一步都可以指示模型调用外部系统、API 或数据库,极大丰富其知识和能力,突破训练数据的局限。这让模型从孤立的个体,演变为更广阔智能系统中的关键组件。
Limitations of single prompts: For multifaceted tasks, using a single, complex prompt for an LLM can be inefficient, causing the model to struggle with constraints and instructions, potentially leading to instruction neglect where parts of the prompt are overlooked, contextual drift where the model loses track of the initial context, error propagation where early errors amplify, prompts which require a longer context window where the model gets insufficient information to respond back and hallucination where the cognitive load increases the chance of incorrect information. For example, a query asking to analyze a market research report, summarize findings, identify trends with data points, and draft an email risks failure as the model might summarize well but fail to extract data or draft an email properly.
单一提示的局限性:对于包含多个子任务的复杂任务,使用单一复杂提示往往效率不高。模型可能难以同时满足多项约束和指示,从而出现以下问题:忽视部分指令、丢失初始上下文、早期错误被放大、上下文超出窗口导致信息不足,以及因认知负担加重而产生幻觉。
例如,要求模型在单次调用中同时完成分析市场报告、总结要点、识别趋势和草拟邮件等多项任务,失败概率极高。模型或许能给出不错的总结,但在提取精确数据或撰写得体邮件这类更细致的环节上,就很容易出错。
Enhanced Reliability Through Sequential Decomposition: Prompt chaining addresses these challenges by breaking the complex task into a focused, sequential workflow, which significantly improves reliability and control. Given the example above, a pipeline or chained approach can be described as follows:
通过顺序分解提升可靠性:提示链通过将复杂任务分解成一个聚焦的、顺序性的工作流,显著提升了可靠性与可控性。以上述例子来说,一个流水线或链式方法可以描述如下:
-
Initial Prompt (Summarization): "Summarize the key findings of the following market research report: [text]." The model's sole focus is summarization, increasing the accuracy of this initial step.
初始提示(总结):"请总结以下市场研究报告的核心发现:[报告文本]。" 模型的唯一焦点是总结,这大大提高了第一步的准确性。
-
Second Prompt (Trend Identification): "Using the summary, identify the top three emerging trends and extract the specific data points that support each trend: [output from step 1]." This prompt is now more constrained and builds directly upon a validated output.
第二个提示(识别趋势):“基于以上总结,请识别出三大新兴趋势,并提取支持每个趋势的具体数据:[第一步的输出]。”这个提示的约束性更强,并且直接建立在一个经过验证的输出之上。
-
Third Prompt (Email Composition): "Draft a concise email to the marketing team that outlines the following trends and their supporting data: [output from step 2]."
第三个提示(撰写邮件):“请起草一封简洁的邮件给市场团队,概述以下趋势及其支持数据:[第二步的输出]。”
This decomposition allows for more granular control over the process. Each step is simpler and less ambiguous, which reduces the cognitive load on the model and leads to a more accurate and reliable final output. This modularity is analogous to a computational pipeline where each function performs a specific operation before passing its result to the next. To ensure an accurate response for each specific task, the model can be assigned a distinct role at every stage. For example, in the given scenario, the initial prompt could be designated as "Market Analyst," the subsequent prompt as "Trade Analyst," and the third prompt as "Expert Documentation Writer," and so forth.
这种分解让我们可以对过程进行更精细的控制。每一步都更简单、更明确,从而降低了模型的认知负荷,带来更准确、更可靠的最终输出。
这种模块化类似于计算流水线:每个函数执行特定操作后,将结果传递给下一步。为了确保每个任务的响应都精确无误,我们还可以在每个阶段为模型赋予不同角色。例如,在上述场景中,初始提示可指定模型扮演「市场分析师」,后续提示指定为「行业分析师」,第三个提示则指定为「专业文档撰写人」。
The Role of Structured Output: The reliability of a prompt chain is highly dependent on the integrity of the data passed between steps. If the output of one prompt is ambiguous or poorly formatted, the subsequent prompt may fail due to faulty input. To mitigate this, specifying a structured output format, such as JSON or XML, is crucial.
结构化输出的作用:提示链的可靠性高度依赖于步骤间传递数据的完整性。如果一个提示的输出模棱两可或格式不佳,后续的提示可能会因错误的输入而失败。为了缓解这一问题,指定一个结构化的输出格式至关重要,例如 JSON 或 XML。
For example, the output from the trend identification step could be formatted as a JSON object:
例如,趋势识别步骤的输出可以格式化为 JSON 对象:
{
"trends": [
{
"trend_name": "AI-Powered Personalization",
"supporting_data": "73% of consumers prefer to do business with brands that use personal information to make their shopping experiences more relevant."
},
{
"trend_name": "Sustainable and Ethical Brands",
"supporting_data": "Sales of products with ESG-related claims grew 28% over the last five years, compared to 20% for products without."
}
]
}
This structured format ensures that the data is machine-readable and can be precisely parsed and inserted into the next prompt without ambiguity. This practice minimizes errors that can arise from interpreting natural language and is a key component in building robust, multi-step LLM-based systems.
这种结构化格式确保数据可被机器读取,能够被精确解析并无歧义地插入到下一个提示中。这样可以减少因解析自然语言而产生的错误,是构建稳健多步骤大语言模型应用的重要环节。
Practical Applications & Use Cases | 实际应用场景
Prompt chaining is a versatile pattern applicable in a wide range of scenarios when building agentic systems. Its core utility lies in breaking down complex problems into sequential, manageable steps. Here are several practical applications:
提示链是一种通用模式,可应用于构建智能体系统的多种场景。其核心效用在于将复杂问题分解为顺序的、可管理的步骤。以下是一些实际应用和用例:
1. Information Processing Workflows: Many tasks involve processing raw information through multiple transformations. For instance, summarizing a document, extracting key entities, and then using those entities to query a database or generate a report. A prompt chain could look like:
信息处理工作流:许多任务涉及对原始信息进行多重转换。例如,总结一份文档,提取关键实体,然后用这些实体查询数据库或生成报告。一个提示链可能如下所示:
-
Prompt 1: Extract text content from a given URL or document.
提示 1: 从给定的 URL 或文档中提取文本内容。
-
Prompt 2: Summarize the cleaned text.
提示 2: 总结清洗后的文本。
-
Prompt 3: Extract specific entities (e.g., names, dates, locations) from the summary or original text.
提示 3: 从总结或原文中提取特定实体(如姓名、日期、地点)。
-
Prompt 4: Use the entities to search an internal knowledge base.
提示 4: 使用这些实体搜索内部知识库。
-
Prompt 5: Generate a final report incorporating the summary, entities, and search results.
提示 5: 结合总结、实体和搜索结果,生成最终报告。
This methodology is applied in domains such as automated content analysis, the development of AI-driven research assistants, and complex report generation.
此方法被广泛应用于自动化内容分析、AI 驱动的研究助手开发以及复杂报告生成等领域。
2. Complex Query Answering: Answering complex questions that require multiple steps of reasoning or information retrieval is a prime use case. For example, "What were the main causes of the stock market crash in 1929, and how did government policy respond?"
复杂问答:回答需要多步推理或信息检索的复杂问题是提示链的典型应用场景。例如,"1929 年股市崩盘的主要原因是什么?政府的应对政策又是什么?"
-
Prompt 1: Identify the core sub-questions in the user's query (causes of crash, government response).
提示 1: 识别用户查询中的核心子问题(崩盘原因、政府对策)。
-
Prompt 2: Research or retrieve information specifically about the causes of the 1929 crash.
提示 2: 研究或检索关于 1929 年崩盘原因的信息。
-
Prompt 3: Research or retrieve information specifically about the government's policy response to the 1929 stock market crash.
提示 3: 研究或检索关于 1929 年股市崩盘的政府对策信息。
-
Prompt 4: Synthesize the information from steps 2 and 3 into a coherent answer to the original query.
提示 4: 将步骤 2 和 3 的信息整合成一个连贯的答案,回答原始问题。
This sequential processing methodology is integral to developing AI systems capable of multi-step inference and information synthesis. Such systems are required when a query cannot be answered from a single data point but instead necessitates a series of logical steps or the integration of information from diverse sources.
这种顺序处理的方法是构建具备多步推理和信息整合能力的 AI 系统的关键。当一个问题无法仅凭单一信息解决,而必须经过一系列逻辑步骤或整合多个信息源才能作答时,这种模式就显得尤为重要。
For example, an automated research agent designed to generate a comprehensive report on a specific topic executes a hybrid computational workflow. Initially, the system retrieves numerous relevant articles. The subsequent task of extracting key information from each article can be performed concurrently for each source. This stage is well-suited for parallel processing, where independent sub-tasks are run simultaneously to maximize efficiency.
例如,一个针对特定主题生成详尽报告的研究智能体会执行混合计算工作流。首先,系统会检索大量相关文章。然后,需要从每篇文章中提取关键信息,这一任务可以针对所有来源并发执行。由于各个提取任务相互独立,这个阶段非常适合采用并行处理,从而实现效率最大化。
However, once the individual extractions are complete, the process becomes inherently sequential. The system must first collate the extracted data, then synthesize it into a coherent draft, and finally review and refine this draft to produce a final report. Each of these later stages is logically dependent on the successful completion of the preceding one. This is where prompt chaining is applied: the collated data serves as the input for the synthesis prompt, and the resulting synthesized text becomes the input for the final review prompt. Therefore, complex operations frequently combine parallel processing for independent data gathering with prompt chaining for the dependent steps of synthesis and refinement.
然而,一旦各自的提取任务完成,整个流程就转变为顺序执行。系统必须先汇集整合所有提取的数据,再将其综合成一份逻辑连贯的初稿,最后对初稿进行审阅和润色,形成最终报告。后续的每一个阶段在逻辑上都依赖于前一阶段的顺利完成,环环相扣。这正是提示链模式发挥作用的时刻:汇集的数据成为后续综合步骤的输入,而综合生成的文本又成为最后审阅步骤的输入。因此,复杂工作流通常采用混合模式:对独立的数据采集任务并行处理,对依赖关系明确的整合与优化步骤使用提示链。
3. Data Extraction and Transformation: The conversion of unstructured text into a structured format is typically achieved through an iterative process, requiring sequential modifications to improve the accuracy and completeness of the output.
数据提取和转换:将非结构化文本转换为结构化格式通常需要一个迭代过程,通过多轮迭代可以提升输出的准确性和完整性。
-
Prompt 1: Attempt to extract specific fields (e.g., name, address, amount) from an invoice document.
提示 1: 尝试从发票中提取特定字段(如姓名、地址、金额)。
-
Processing: Check if all required fields were extracted and if they meet format requirements.
处理:检查是否提取了所有必需的字段,以及是否符合格式要求。
-
Prompt 2 (Conditional): If fields are missing or malformed, craft a new prompt asking the model to specifically find the missing/malformed information, perhaps providing context from the failed attempt.
提示 2(条件判断):如果字段缺失或格式不正确,构建一个新提示,要求模型专门查找缺失或处理格式不正确的信息,并可提供上一次失败的上下文。
-
Processing: Validate the results again. Repeat if necessary.
处理:再次验证结果。如有必要,重复此过程。
-
Output: Provide the extracted, validated structured data.
输出:提供经过验证的结构化数据。
This sequential processing methodology is particularly applicable to data extraction and analysis from unstructured sources like forms, invoices, or emails. For example, solving complex Optical Character Recognition (OCR) problems, such as processing a PDF form, is more effectively handled through a decomposed, multi-step approach.
这种顺序处理的方法论,尤其适用于从表单、发票或邮件等非结构化来源中进行数据提取与分析。例如,在对 PDF 进行 OCR 识别时,采用分解式的多步方法会远比单次请求更为有效。
Initially, a large language model is employed to perform the primary text extraction from the document image. Following this, the model processes the raw output to normalize the data, a step where it might convert numeric text, such as "one thousand and fifty," into its numerical equivalent, 1050. A significant challenge for LLMs is performing precise mathematical calculations. Therefore, in a subsequent step, the system can delegate any required arithmetic operations to an external calculator tool. The LLM identifies the necessary calculation, feeds the normalized numbers to the tool, and then incorporates the precise result. This chained sequence of text extraction, data normalization, and external tool use achieves a final, accurate result that is often difficult to obtain reliably from a single LLM query.
首先,系统调用大语言模型从图像中提取文本。随后,模型处理这些原始输出进行数据规范化,比如将「一千零五十」这样的文本转换为数值 1050。由于精确数学计算对大语言模型来说是一项挑战,在后续步骤中,系统会将需要的算术运算交给外部计算器执行。模型负责识别需要的运算,将规范化后的数字传递给计算工具,然后将精确结果整合回来。通过文本提取、数据规范化、外部工具调用的链式流程,系统可获得精确结果,这是单次模型调用难以实现的。
4. Content Generation Workflows: The composition of complex content is a procedural task that is typically decomposed into distinct phases, including initial ideation, structural outlining, drafting, and subsequent revision.
内容生成工作流:复杂内容的创作通常被分解为不同阶段,包括初步构思、搭建大纲、起草和修订等。
-
Prompt 1: Generate 5 topic ideas based on a user's general interest.
提示 1: 基于用户的兴趣爱好,生成 5 个主题。
-
Processing: Allow the user to select one idea or automatically choose the best one.
处理:允许用户选择一个主题或自动选择最好的一个。
-
Prompt 2: Based on the selected topic, generate a detailed outline.
提示 2: 基于选定的主题,生成详细的大纲。
-
Prompt 3: Write a draft section based on the first point in the outline.
提示 3: 基于大纲的第一点,撰写初稿。
-
Prompt 4: Write a draft section based on the second point in the outline, providing the previous section for context. Continue this for all outline points.
提示 4: 在提供前一部分上下文的情况下,根据大纲的第二点撰写草稿,并以此类推完成所有要点。
-
Prompt 5: Review and refine the complete draft for coherence, tone, and grammar.
提示 5: 审阅和润色完整的初稿,确保连贯性、语气和语法。
This methodology is employed for a range of natural language generation tasks, including the automated composition of creative narratives, technical documentation, and other forms of structured textual content.
这种方法适用于多种自然语言生成任务,比如自动撰写创意故事、编写技术文档以及生成其他结构化文本内容。
5. Conversational Agents with State: Although comprehensive state management architectures employ methods more complex than sequential linking, prompt chaining provides a foundational mechanism for preserving conversational continuity. This technique maintains context by constructing each conversational turn as a new prompt that systematically incorporates information or extracted entities from preceding interactions in the dialogue sequence.
有状态的对话智能体:虽然完善的状态管理架构需要比顺序链接更复杂的方法,但提示链为维持对话连续性提供了基础机制。核心思想是将每轮对话构建为新提示,系统性地融入先前交互产生的信息或提取的实体。
-
Prompt 1: Process User Utterance 1, identify intent and key entities.
提示 1: 处理用户的第一轮发言,识别意图和关键实体。
-
Processing: Update conversation state with intent and entities.
处理:更新对话状态,包含意图和实体。
-
Prompt 2: Based on current state, generate a response and/or identify the next required piece of information.
提示 2: 基于当前状态,生成响应或识别下一个所需的信息。
-
Repeat for subsequent turns, with each new user utterance initiating a chain that leverages the accumulating conversation history (state).
在后续的对话中重复此过程,用户的每一句新话语都会启动一个新的处理链,并充分利用不断积累的对话历史(即状态)。
This principle is fundamental to the development of conversational agents, enabling them to maintain context and coherence across extended, multi-turn dialogues. By preserving the conversational history, the system can understand and appropriately respond to user inputs that depend on previously exchanged information.
这一原则对于开发对话智能体至关重要,使智能体在多轮对话中保持上下文理解和逻辑连贯性。通过保留对话历史,系统就能够理解并恰当地回应那些依赖于先前交换信息的后续输入。
6. Code Generation and Refinement: The generation of functional code is typically a multi-stage process, requiring a problem to be decomposed into a sequence of discrete logical operations that are executed progressively
代码生成和优化:功能性代码的生成通常是一个多阶段的过程,它要求将问题分解为一系列可有序执行的逻辑操作。
-
Prompt 1: Understand the user's request for a code function. Generate pseudocode or an outline.
提示 1: 理解用户的需求,生成伪代码或大纲。
-
Prompt 2: Write the initial code draft based on the outline.
提示 2: 基于大纲,编写初始版本的代码。
-
Prompt 3: Identify potential errors or areas for improvement in the code (perhaps using a static analysis tool or another LLM call).
提示 3: 识别代码中可能存在的错误或需要改进的地方(使用静态分析工具或另外调用一次模型)。
-
Prompt 4: Rewrite or refine the code based on the identified issues.
提示 4: 基于识别出的问题,重写或优化代码。
-
Prompt 5: Add documentation or test cases.
提示 5: 添加文档或测试用例。
In applications such as AI-assisted software development, the utility of prompt chaining stems from its capacity to decompose complex coding tasks into a series of manageable sub-problems. This modular structure reduces the operational complexity for the large language model at each step. Critically, this approach also allows for the insertion of deterministic logic between model calls, enabling intermediate data processing, output validation, and conditional branching within the workflow. By this method, a single, multifaceted request that could otherwise lead to unreliable or incomplete results is converted into a structured sequence of operations managed by an underlying execution framework.
在 AI 辅助软件开发等应用中,提示链的价值在于将复杂编码任务分解为一系列可管理的子问题,这种模块化结构降低了模型在每一步的复杂度。更重要的是,这种方法允许我们在两次模型调用之间插入确定性逻辑,从而在工作流中实现中间数据处理、输出验证和条件分支等功能。通过这种方式,一个原本可能导致不可靠或不完整结果的单一复杂请求,被转化为由底层执行框架管理的结构化操作序列。
7. Multimodal and multi-step reasoning: Analyzing datasets with diverse modalities necessitates breaking down the problem into smaller, prompt-based tasks. For example, interpreting an image that contains a picture with embedded text, labels highlighting specific text segments, and tabular data explaining each label, requires such an approach.
多模态和多步推理:分析包含多种模态(如图像、文本、表格)的数据时,必须将问题分解为更小的、基于提示的任务。例如,要解读一张复杂的图像,其中不仅有图片和文本,还有对特定文本段的高亮标注,以及采用表格来解释每个标签的情况,就需要采用这样的方法。
-
Prompt 1: Extract and comprehend the text from the user's image request.
提示 1: 从用户的图像请求中提取并理解文本内容。
-
Prompt 2: Link the extracted image text with its corresponding labels.
提示 2: 将提取出的图像文本与其对应的标签进行关联。
-
Prompt 3: Interpret the gathered information using a table to determine the required output.
提示 3: 利用表格来解读已收集到的信息,以确定最终需要输出的内容。
Hands-On Code Example | 实践示例
Implementing prompt chaining ranges from direct, sequential function calls within a script to the utilization of specialized frameworks designed to manage control flow, state, and component integration. Frameworks such as LangChain, LangGraph, Crew AI, and the Google Agent Development Kit (ADK) offer structured environments for constructing and executing these multi-step processes, which is particularly advantageous for complex architectures.
实现提示链的方法有很多,从直接在脚本中依次调用函数,到利用专门的框架来管理控制流、状态和组件集成,形式不一。像 LangChain、LangGraph、Crew AI 以及谷歌智能体开发套件(ADK)这类框架,能为构建和执行多步流程提供结构化的环境,这对于复杂的系统架构尤其有益。
For the purpose of demonstration, LangChain and LangGraph are suitable choices as their core APIs are explicitly designed for composing chains and graphs of operations. LangChain provides foundational abstractions for linear sequences, while LangGraph extends these capabilities to support stateful and cyclical computations, which are necessary for implementing more sophisticated agentic behaviors. This example will focus on a fundamental linear sequence.
为了演示,LangChain 和 LangGraph 是非常合适的选择,因为它们的核心 API 就是为组合操作链(Chains)和图(Graphs)而设计的。LangChain 为线性序列提供了基础的抽象,而 LangGraph 则在此基础上进一步扩展,支持有状态和循环计算,这对于实现更复杂的智能体行为至关重要。本示例将聚焦于一个基础的线性序列。
The following code implements a two-step prompt chain that functions as a data processing pipeline. The initial stage is designed to parse unstructured text and extract specific information. The subsequent stage then receives this extracted output and transforms it into a structured data format.
下面的代码实现了一个两步的提示链,它就像一个数据处理流水线。第一步旨在解析非结构化文本并提取特定信息;第二步则接收上一步的输出,并将其转换为结构化的数据格式。
To replicate this procedure, the required libraries must first be installed. This can be accomplished using the following command:
要运行此示例,首先需要安装必要的库:
pip install langchain langchain-community langchain-openai langgraph
Note that langchain-openai can be substituted with the appropriate package for a different model provider. Subsequently, the execution environment must be configured with the necessary API credentials for the selected language model provider, such as OpenAI, Google Gemini, or Anthropic.
请注意,langchain-openai 可以替换为其他模型提供商的相应库包。此外,你必须在运行环境中配置好所选语言模型(如 OpenAI、Google Gemini 或 Anthropic)的 API 密钥。
import os
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
# For better security, load environment variables from a .env file
# 为了更好的安全性,建议从 .env 文件加载环境变量
# from dotenv import load_dotenv
# load_dotenv()
# Make sure your OPENAI_API_KEY is set in the .env file
# 确保你的 OPENAI_API_KEY 已在 .env 文件中设置
# Initialize the Language Model (using ChatOpenAI is recommended)
# 初始化语言模型(推荐使用 ChatOpenAI)
llm = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0)
# --- Prompt 1: Extract Information ---
# --- 提示 1: 提取信息 ---
prompt_extract = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(
"Extract the technical specifications from the following text:\n\n{text_input}"
)
# --- Prompt 2: Transform to JSON ---
# --- 提示 2: 转换为 JSON ---
prompt_transform = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(
"Transform the following specifications into a JSON object with 'cpu', 'memory', and 'storage' as keys:\n\n{specifications}"
)
# --- Build the Chain using LCEL ---
# The StrOutputParser() converts the LLM's message output to a simple string.
# --- 使用 LCEL 构建链 ---
# StrOutputParser() 会将 LLM 的消息输出转换为一个简单的字符串。
extraction_chain = prompt_extract | llm | StrOutputParser()
# The full chain passes the output of the extraction chain into the 'specifications'
# variable for the transformation prompt.
# 完整的链将提取链的输出传递给转换提示中的 'specifications' 变量。
full_chain = (
{"specifications": extraction_chain}
| prompt_transform
| llm
| StrOutputParser()
)
# --- Run the Chain ---
# --- 运行链 ---
input_text = "The new laptop model features a 3.5 GHz octa-core processor, 16GB of RAM, and a 1TB NVMe SSD."
# Execute the chain with the input text dictionary.
# 接收输入文本并执行链。
final_result = full_chain.invoke({"text_input": input_text})
print("\n--- Final JSON Output ---")
# print("\n--- 打印最终输出的 JSON ---")
print(final_result)
运行输出(译者添加):
--- Final JSON Output ---
{
"cpu": "3.5 GHz octa-core",
"memory": "16GB",
"storage": "1TB NVMe SSD"
}
This Python code demonstrates how to use the LangChain library to process text. It utilizes two separate prompts: one to extract technical specifications from an input string and another to format these specifications into a JSON object. The ChatOpenAI model is employed for language model interactions, and the StrOutputParser ensures the output is in a usable string format. The LangChain Expression Language (LCEL) is used to elegantly chain these prompts and the language model together. The first chain, extraction_chain, extracts the specifications. The full_chain then takes the output of the extraction and uses it as input for the transformation prompt. A sample input text describing a laptop is provided. The full_chain is invoked with this text, processing it through both steps. The final result, a JSON string containing the extracted and formatted specifications, is then printed.
这段 Python 代码演示了如何使用 LangChain 库来处理文本。它利用了两个独立的提示:一个从输入字符串中提取技术规格,另一个将这些规格格式化为 JSON 对象。ChatOpenAI 模型被用来与语言模型进行交互,StrOutputParser 确保输出是可直接使用的字符串格式。LangChain 表达式语言(LCEL),也就是代码中的 | 符号,被用来优雅地将这些组件「链接」在一起。代码首先构建了一个 extraction_chain,负责提取规格。然后,full_chain 接收前一个链的输出,并将其作为输入传给负责转换格式的提示。最后,我们提供了一段描述笔记本电脑的示例文本,并通过 invoke 方法让 full_chain 按顺序执行这两个步骤,打印出最终提取并格式化好的 JSON 字符串。
Context Engineering and Prompt Engineering | 上下文工程和提示工程
Context Engineering (see Fig.1) is the systematic discipline of designing, constructing, and delivering a complete informational environment to an AI model prior to token generation. This methodology asserts that the quality of a model's output is less dependent on the model's architecture itself and more on the richness of the context provided.
上下文工程(Context Engineering,见图 1)是一门系统性的学科,它研究的是在 AI 模型生成词元(Token)之前,如何为其设计、构建并提供一个完整的信息环境。这一方法论主张,模型输出的质量与其说取决于模型自身的架构,不如说更依赖于所提供上下文的丰富程度。
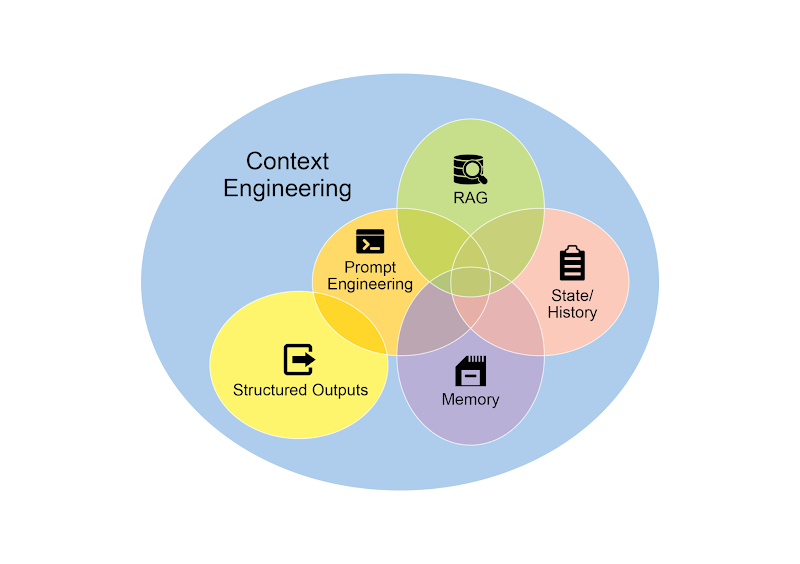
Fig.1: Context Engineering is the discipline of building a rich, comprehensive informational environment for an AI, as the quality of this context is a primary factor in enabling advanced Agentic performance.
图 1:上下文工程是一门为 AI 构建丰富、全面信息环境的学科,因为高质量的上下文是实现高级智能体性能的首要因素。
It represents a significant evolution from traditional prompt engineering, which focuses primarily on optimizing the phrasing of a user's immediate query. Context Engineering expands this scope to include several layers of information, such as the system prompt, which is a foundational set of instructions defining the AI's operational parameters—for instance, "You are a technical writer; your tone must be formal and precise." The context is further enriched with external data. This includes retrieved documents, where the AI actively fetches information from a knowledge base to inform its response, such as pulling technical specifications for a project. It also incorporates tool outputs, which are the results from the AI using an external API to obtain real-time data, like querying a calendar to determine a user's availability. This explicit data is combined with critical implicit data, such as user identity, interaction history, and environmental state. The core principle is that even advanced models underperform when provided with a limited or poorly constructed view of the operational environment.
它代表了对传统提示工程(Prompt Engineering)的一次重大演进,后者主要聚焦于优化用户当前调用的输入。上下文工程则将这一范畴大大拓宽,囊括了多个信息层面。比如系统提示(System Prompt)可以作为一套基础指令,用来定义 AI 的运行参数,比如「你是一位技术文档撰写者,你的语气必须正式且精准」。
上下文还会通过外部数据得到进一步丰富。这包括检索到的文档,即 AI 主动从知识库中获取信息以支撑其回答,例如获取一个项目的技术规范。它同样也包含工具输出,这来源于 AI 调用外部接口获取实时数据,比如查询日历以确定用户的空闲时间。这些显式数据会与关键的隐式数据(如用户身份、交互历史和环境状态)相结合。其核心原则是:即便是最先进的模型,如果提供给它的运行环境视图是有限或结构不良的,其表现也会大打折扣。
This practice, therefore, reframes the task from merely answering a question to building a comprehensive operational picture for the agent. For example, a context-engineered agent would not just respond to a query but would first integrate the user's calendar availability (a tool output), the professional relationship with an email's recipient (implicit data), and notes from previous meetings (retrieved documents). This allows the model to generate outputs that are highly relevant, personalized, and pragmatically useful. The "engineering" component involves creating robust pipelines to fetch and transform this data at runtime and establishing feedback loops to continually improve context quality.
因此,这种实践将任务的重点从仅仅回答问题重构为为智能体构建全面的操作全貌。举例来说,一个经过上下文工程的智能体不会只是简单地回应查询,而是会首先整合用户的空闲时间(工具输出)、与邮件接收者的职业关系(隐式数据)以及过往的会议纪要(检索到的文档)。这使得模型能够生成高度相关、个性化且具有实际价值的输出。「工程」二字体现在创建稳定的流水线,以便在运行时获取和转换这些数据,并建立反馈循环来持续提升上下文的质量。
To implement this, specialized tuning systems can be used to automate the improvement process at scale. For example, tools like Google's Vertex AI prompt optimizer can enhance model performance by systematically evaluating responses against a set of sample inputs and predefined evaluation metrics. This approach is effective for adapting prompts and system instructions across different models without requiring extensive manual rewriting. By providing such an optimizer with sample prompts, system instructions, and a template, it can programmatically refine the contextual inputs, offering a structured method for implementing the feedback loops required for sophisticated Context Engineering.
为了实现这一点,我们可以使用专门的调优系统来大规模自动化这一改进过程。例如,像谷歌的 Vertex AI 提示优化器这类工具,可以通过系统性地评估模型响应(基于一组样本输入和预定义的评估指标)来提升模型性能。这种方法能有效地让提示和系统指令适配不同的模型,而无需大量手动重写。通过为这类优化器提供样本提示、系统指令和一个模板,它就能够程序化地优化上下文输入,为实现复杂的上下文工程所需的反馈循环提供一种结构化的方法。
This structured approach is what differentiates a rudimentary AI tool from a more sophisticated and contextually-aware system. It treats the context itself as a primary component, placing critical importance on what the agent knows, when it knows it, and how it uses that information. The practice ensures the model has a well-rounded understanding of the user's intent, history, and current environment. Ultimately, Context Engineering is a crucial methodology for advancing stateless chatbots into highly capable, situationally-aware systems.
正是这种结构化的方法,将一个基础的 AI 工具与一个更复杂、更具上下文感知能力的系统区分开来。它将上下文本身视为一个核心组件,极度重视智能体知道什么、何时知道以及如何使用这些信息。这一实践的核心是确保模型能全面洞悉用户的意图、历史背景及其当前所处的环境。归根结底,上下文工程是将无状态的聊天机器人提升为能力强大、具备情境感知能力系统的关键方法论。
At a Glance | 要点速览
What: Complex tasks often overwhelm LLMs when handled within a single prompt, leading to significant performance issues. The cognitive load on the model increases the likelihood of errors such as overlooking instructions, losing context, and generating incorrect information. A monolithic prompt struggles to manage multiple constraints and sequential reasoning steps effectively. This results in unreliable and inaccurate outputs, as the LLM fails to address all facets of the multifaceted request.
问题所在:用单个提示处理复杂任务,往往会让大语言模型不堪重负,导致性能骤降。过高的认知负荷会增加模型出错的概率,例如忽略指令、丢失上下文、生成错误信息等。这种大而全的指令,很难有效管理多个约束条件和环环相扣的推理步骤,最终导致输出结果既不可靠,也不准确。
Why: Prompt chaining provides a standardized solution by breaking down a complex problem into a sequence of smaller, interconnected sub-tasks. Each step in the chain uses a focused prompt to perform a specific operation, significantly improving reliability and control. The output from one prompt is passed as the input to the next, creating a logical workflow that progressively builds towards the final solution. This modular, divide-and-conquer strategy makes the process more manageable, easier to debug, and allows for the integration of external tools or structured data formats between steps. This pattern is foundational for developing sophisticated, multi-step Agentic systems that can plan, reason, and execute complex workflows.
解决之道:提示链模式的精髓在于化整为零,它将一个复杂的问题分解为一系列更小、且环环相扣的子任务,从而提供了一套标准化的解法。链条中的每一步都使用一个高度聚焦的提示来执行特定操作,极大地提升了可靠性与可控性。上一步的输出会作为下一步的输入,由此创建出一个逻辑清晰的工作流,逐步构建出最终的解决方案。这种模块化的策略,让整个过程更易于管理和调试,并允许在步骤之间集成外部工具或结构化数据。该模式是开发能够规划、推理和执行复杂工作流的高级智能体系统的基础。
Rule of thumb: Use this pattern when a task is too complex for a single prompt, involves multiple distinct processing stages, requires interaction with external tools between steps, or when building Agentic systems that need to perform multi-step reasoning and maintain state.
适用场景:如果一项任务过于复杂,单个提示难以胜任;或涉及多个独立的处理步骤;或需要在步骤间与外部工具交互;亦或在构建需要多步推理和状态维持的智能体系统时,都可考虑使用此模式。
Visual summary | 可视化总结
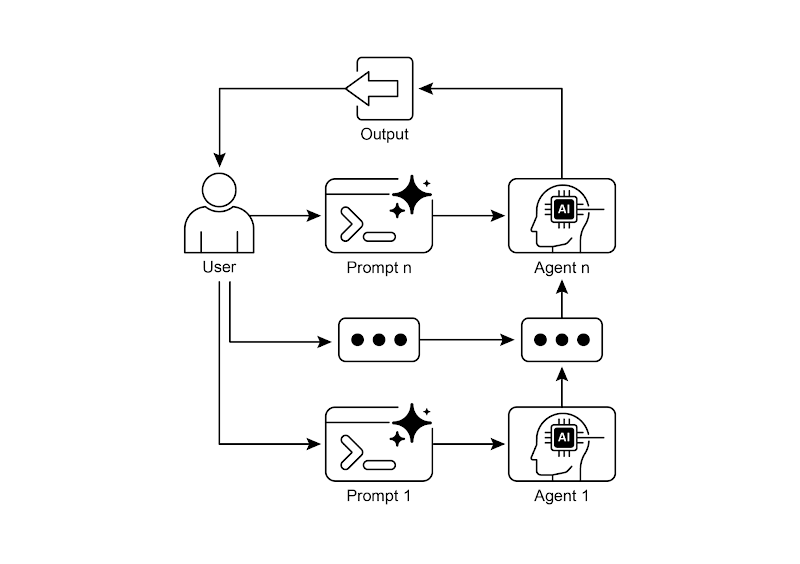
Fig. 2: Prompt Chaining Pattern: Agents receive a series of prompts from the user, with the output of each agent serving as the input for the next in the chain.
图 2:提示链模式 —— 智能体从用户处接收一系列提示,链条中前一个智能体的输出,会成为下一个智能体的输入。
Key Takeaways | 核心要点
Here are some key takeaways:
以下是本章的核心要点:
-
Prompt Chaining breaks down complex tasks into a sequence of smaller, focused steps. This is occasionally known as the Pipeline pattern.
提示链将复杂任务分解为一系列更小、更聚焦的步骤,也被称为流水线模式(Pipeline Pattern)。
-
Each step in a chain involves an LLM call or processing logic, using the output of the previous step as input.
-
链条中的每一步都涉及一次大语言模型调用或特定的处理逻辑,并以上一步的输出作为输入。
-
This pattern improves the reliability and manageability of complex interactions with language models.
-
此模式能够提升与语言模型进行复杂交互时的可靠性与可管理性。
-
Frameworks like LangChain/LangGraph, and Google ADK provide robust tools to define, manage, and execute these multi-step sequences.
-
像 LangChain/LangGraph 和谷歌智能体开发套件(ADK)这类框架,为定义、管理和执行这些多步序列提供了强大的工具。
Conclusion | 结语
By deconstructing complex problems into a sequence of simpler, more manageable sub-tasks, prompt chaining provides a robust framework for guiding large language models. This "divide-and-conquer" strategy significantly enhances the reliability and control of the output by focusing the model on one specific operation at a time. As a foundational pattern, it enables the development of sophisticated AI agents capable of multi-step reasoning, tool integration, and state management. Ultimately, mastering prompt chaining is crucial for building robust, context-aware systems that can execute intricate workflows well beyond the capabilities of a single prompt.
通过将复杂问题解构为一系列更简单、更易于管理的子任务,提示链为驾驭大语言模型提供了一个稳健的框架。这种「分而治之」的策略,通过让模型在同一时间只专注于一个特定操作,显著增强了输出结果的可靠性与可控性。
作为一项基础性模式,它为开发能够进行多步推理、工具集成和状态管理的高级 AI 智能体铺平了道路。归根结底,掌握提示链是构建那些能够执行复杂工作流、能力远超单一提示、具备上下文感知能力的强大系统的关键所在。
References | 参考文献
-
LangChain Documentation on LCEL: https://python.langchain.com/v0.2/docs/core_modules/expression_language/
LangChain LCEL 的官方文档:https://python.langchain.com/v0.2/docs/core_modules/expression_language/
-
LangGraph Documentation: https://langchain-ai.github.io/langgraph/
LangGraph 官方文档:https://langchain-ai.github.io/langgraph/
-
Prompt Engineering Guide - Chaining Prompts: https://www.promptingguide.ai/techniques/chaining
提示工程指南 - 链式提示:https://www.promptingguide.ai/techniques/chaining
-
OpenAI API Documentation: https://platform.openai.com/docs/guides/gpt/prompting
OpenAI API 官方文档:https://platform.openai.com/docs/guides/gpt/prompting
-
Crew AI Documentation: https://docs.crewai.com/
Crew AI 官方文档:https://docs.crewai.com/
-
Google AI for Developers: https://cloud.google.com/discover/what-is-prompt-engineering?hl=en
谷歌 AI 开发者中心:https://cloud.google.com/discover/what-is-prompt-engineering?hl=en
-
Vertex Prompt Optimizer: https://cloud.google.com/vertex-ai/generative-ai/docs/learn/prompts/prompt-optimizer
Vertex AI 提示优化器:https://cloud.google.com/vertex-ai/generative-ai/docs/learn/prompts/prompt-optimizer